@yasmit/md-links
v1.0.3
Published
Read and analyze files in Markdown format and verify the links they contain and report some statistics.
Downloads
3
Maintainers
Readme
Descripción
Markdown es un lenguaje de marcado
ligero muy popular entre developers. Es usado en muchísimas plataformas que
manejan texto plano (GitHub, foros, blogs, ...), y es muy común
encontrar varios archivos en ese formato en cualquier tipo de repositorio
(empezando por el tradicional README.md).
Estos archivos Markdown normalmente contienen links (vínculos/ligas) que
muchas veces están rotos o ya no son válidos y eso perjudica mucho el valor de
la información que se quiere compartir.
El objetivo es crear una herramienta usando Node.js, que lea y analice archivos en formato Markdown, para verificar los links que contengan y reportar algunas estadísticas.
Diagrama de Flujo
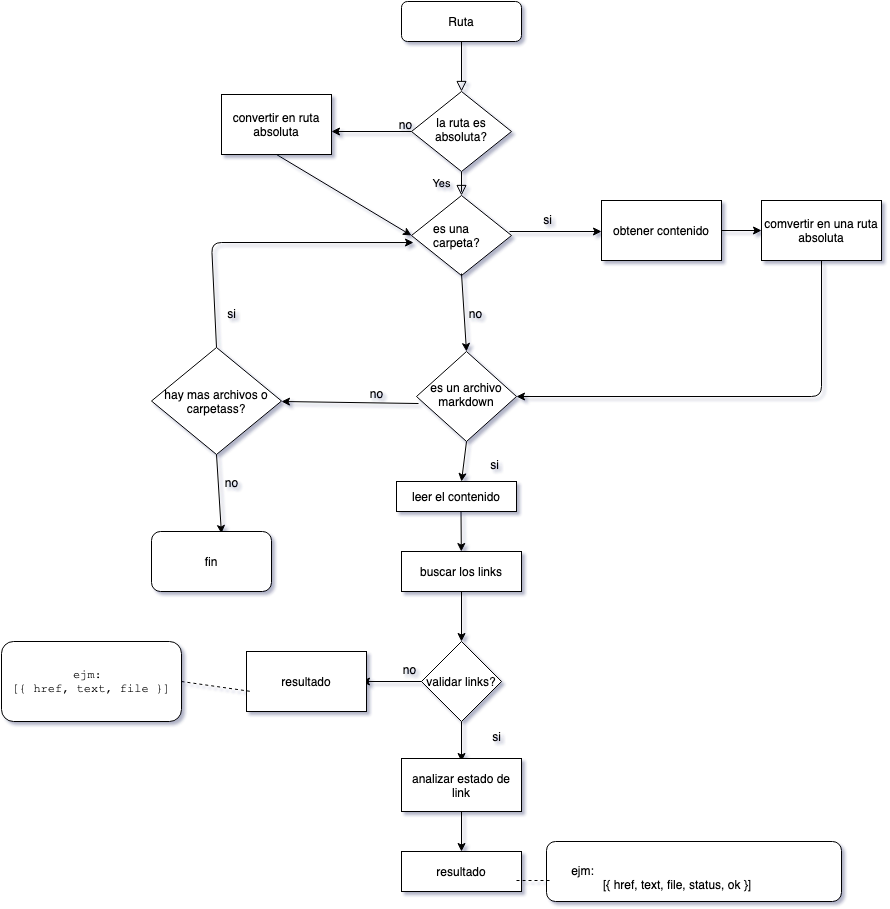
Instalación y guía de uso de la librería
Para usar este proyecto, lo primero que debe hacer es instalar la librería. Para ello ejecute en la terminal la siguiente línea de comando:
npm install YasmitDaysi/LIM011-fe-md-links
- Importando el módulo con require para usarlo programáticamente:
const mdLinks = require("md-links")API
mdLinks(path, options)
path:Tipo de dato string que representa la ruta absoluta o relativa al archivo o directorio. Si la ruta pasada es relativa, se resuelve como relativa al directorio desde donde se invoca node - current working directory).options:Un objeto con las seguientes propiedades.
{validate: booleano}.
{stats:booleano}.
{stats:booleano},{validate:booleano}.Valor de retorno
La función retornar una promesa (Promise) que resuelva a un arreglo
(Array) de objetos (Object), donde cada objeto representa un link y contiene
las siguientes propiedades:
href: URL encontrada.text: Texto que aparecía dentro del link .file: Ruta del archivo donde se encontró el link.
Ejemplo:
const mdLinks = require("md-links");
mdLinks("./some/example.md")
.then(links => {
// [{ href, text, file }]
})
mdLinks("./some/example.md", { validate: true })
.then(links => {
// [{ href, text, file, status, ok }]
})
mdLinks("./some/example.md", { stats: true })
.then(links => {
// Total: 3
// Unique: 3
})
mdLinks("./some/example.md", { stats: true, validate: true })
.then(links => {
// Total: 3
// Unique: 3
// Broken: 1
}) A través de la terminal:
md-links <path-to-file> {options};
Donde:
- path-to-file: Es la ruta absoluta o relativa al archivo o directorio que desea analizar.
- options: Se tiene las siguientes opciones para ejecutar en la linea de comando:
--validate--stats--stats --validate juntos
ejemplos:
- $ md-links ./some/example.md
./some/example.md http://algo.com/2/3/ Link a algo
./some/example.md https://otra-cosa.net/algun-doc.html algún doc
./some/example.md http://google.com/ Google- $ md-links ./some/example.md --validate
./some/example.md http://algo.com/2/3/ ok 200 Link a algo
./some/example.md https://otra-cosa.net/algun-doc.html fail 404 algún doc
./some/example.md http://google.com/ ok 301 Google- $ md-links ./some/example.md --stats
Total: 3
Unique: 3-$ md-links ./some/example.md --stats --validate
Total: 3
Unique: 3
Broken: 1LICENCIA
- Licencia Copyright (c) 2020, yasmit vasquez Licencia MIT.
