@tensorflow-models/hand-pose-detection
v2.0.1
Published
Pretrained hand pose detection model
Keywords
Readme
Hand Pose Detection
This package provides models for running real-time hand pose detection.
Currently, we provide 1 model option:
MediaPipe:
MediaPipe Hands can detect multiple hands, each hand contains 21 3D hand keypoints.
More background information about the model, as well as its performance characteristics on different datasets, can be found here: Model Card
Table of Contents
How to Run It
In general there are two steps:
You first create a detector by choosing one of the models from SupportedModels,
including MediaPipeHands.
For example:
const model = handPoseDetection.SupportedModels.MediaPipeHands;
const detectorConfig = {
runtime: 'mediapipe', // or 'tfjs',
solutionPath: 'https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/@mediapipe/hands',
modelType: 'full'
}
const detector = await handPoseDetection.createDetector(model, detectorConfig);Then you can use the detector to detect hands.
const hands = await detector.estimateHands(image);The returned hands list contains detected hands for each hand in the image. If the model cannot detect any hands, the list will be empty.
For each hand, it contains a prediction of the handedness (left or right), a confidence score of this prediction, as well as an array of keypoints. MediaPipeHands returns 21 keypoints. Each keypoint contains x and y, as well as a name. In addition, an array of 3D keypoints is returned.
Example output:
[
{
score: 0.8,
handedness: ‘Right’,
keypoints: [
{x: 105, y: 107, name: "wrist"},
{x: 108, y: 160, name: "pinky_finger_tip"},
...
],
keypoints3D: [
{x: 0.00388, y: -0.0205, z: 0.0217, name: "wrist"},
{x: -0.025138, y: -0.0255, z: -0.0051, name: "pinky_finger_tip"},
...
]
}
]The score ranges from 0 to 1. It represents the model's confidence of the detected hand.
handedness is set to either 'Left' or 'Right', which is the model prediction of the detected hand's handedness.
For the keypoints, x and y represent the actual keypoint position in the image pixel space.
For the keypoints3D, x, y and z represent absolute distance in a metric scale, where the origin is formed as an average between the first knuckles of index, middle, ring and pinky fingers.
The name provides a label for each keypoint, such as 'wrist', 'pinky_finger_tip', etc.
Refer to each model's documentation for specific configurations for the model and their performance.
MediaPipeHands MediaPipe Documentation
MediaPipeHands TFJS Documentation
Keypoint Diagram
See the diagram below for what those keypoints are and their index in the array.
MediaPipe Hands Keypoints: Used in MediaPipe Hands
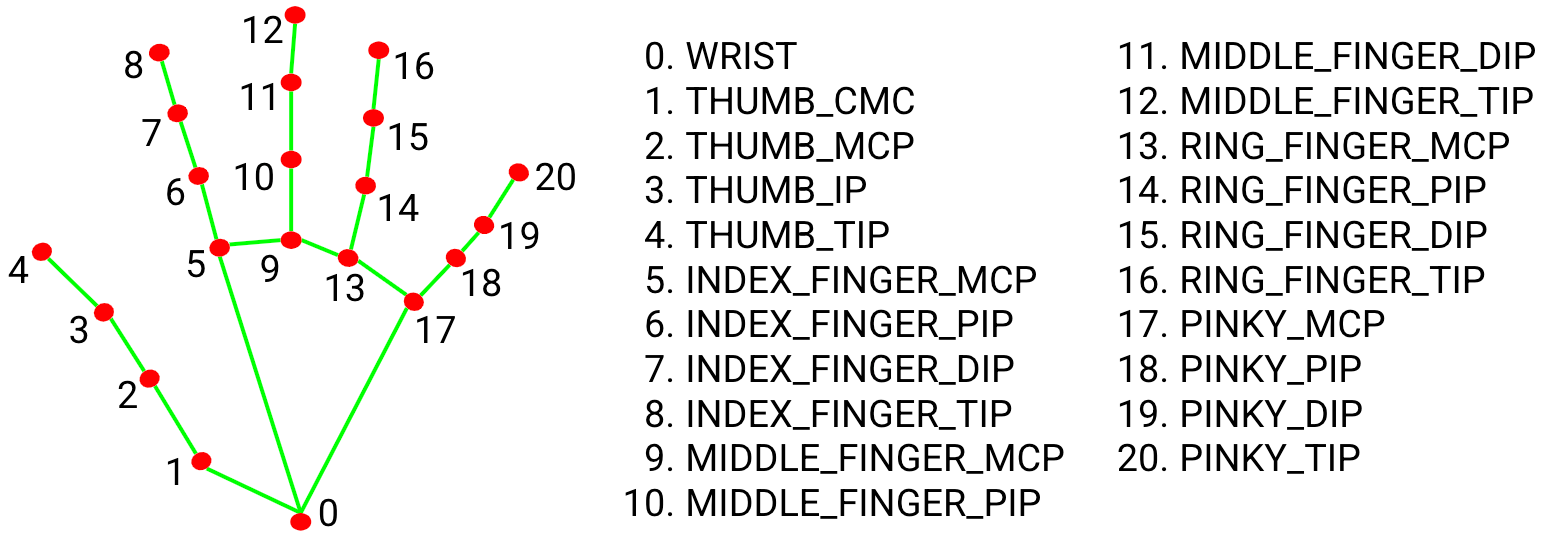 0: wrist
0: wrist
1: thumb_cmc
2: thumb_mcp
3: thumb_ip
4: thumb_tip
5: index_finger_mcp
6: index_finger_pip
7: index_finger_dip
8: index_finger_tip
9: middle_finger_mcp
10: middle_finger_pip
11: middle_finger_dip
12: middle_finger_tip
13: ring_finger_mcp
14: ring_finger_pip
15: ring_finger_dip
16: ring_finger_tip
17: pinky_finger_mcp
18: pinky_finger_pip
19: pinky_finger_dip
20: pinky_finger_tip
Example Code and Demos
You may reference the demos for code examples. Details for how to run the demos
are included in the demos/
folder.
