@sara-rioseco/md-links
v1.0.4
Published
Md-links module is a CLI application that can be used to retrieve all links, inside markdown files that are present in a specific path.
Downloads
31
Readme
MD-Links 🔗
Contents
- 1. Introduction
- 2. Project definition
- 3. User guide
- 4. Unit tests
- 5. Planning
- 6. Requirements checklist
- 7. Tools and skills
1. Introduction ✈️
Markdown is an lightweight markup language that is used with plain text to add formatting elements (headings, bulleted lists, URLs) to text without the use of a formal text editor or the use of HTML tags. Markdown is used in many platforms that handle plain text, such as Slack, forums, blogs, among others, so it's very common to find several files using this format in different kinds of repositories. We don't need to go that far to find examples of this, for instance, the classic README file, such as this very one, uses Markdown and you can verify that by checking the file's extension, which is ".md" and stands for Markdown documentation.
Usually these .md files, contains links that are often broken, or no longer accessible. This situation diminish the value of the information you are trying to share. That's why this project intends to tackle that problem by reading and analyzing Markdown files, verifying the links inside of them and creating a report with these links' stats.

2. Project definition 🚀
This module is a library that can be used to retrieve all links, inside all markdown files that are present in a specific path (folder or file). Besides that, you can check the status of all the links retrieved and see a summary with the stats found on the analysis. Node JS was the javascript framework chosen to develop this tool. You can use this library as CLI application or as an API.
This library and the CLI use external libraries as dependencies (such as the path module, the FS module, the HTTP client Axios, and the terminal string styling API Chalk) and were developed with Javascript to be run with NodeJS. Babel, Eslint and Jest were also used for the developing/testing stages.
3. User guide 📖
As a CLI (Command-Line Application)
Installation
Open your terminal and run the following command:
npm i @sara-rioseco/md-linksHow to use
Once the installation is complete, run the following command in your terminal:
npx @sara-rioseco/md-links <path> [options]Where path is the route to the file or directory (it can be an absolute or relative path), and options are the additional actions you want to perform. Options are non mandatory, and the application will still run if only a path is provided. Possible options are: --validate, --stats, or both.
Expected output
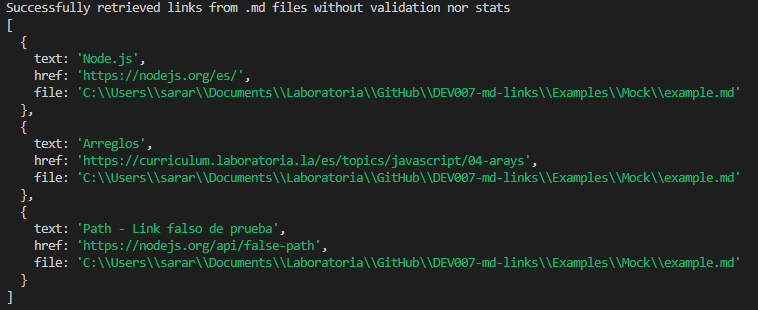
No options: if no options are entered , the application will show you all the links found in that path. If the path is not valid, or no .md file is found and error will appear.
npx @sara-rioseco/md-links <path>
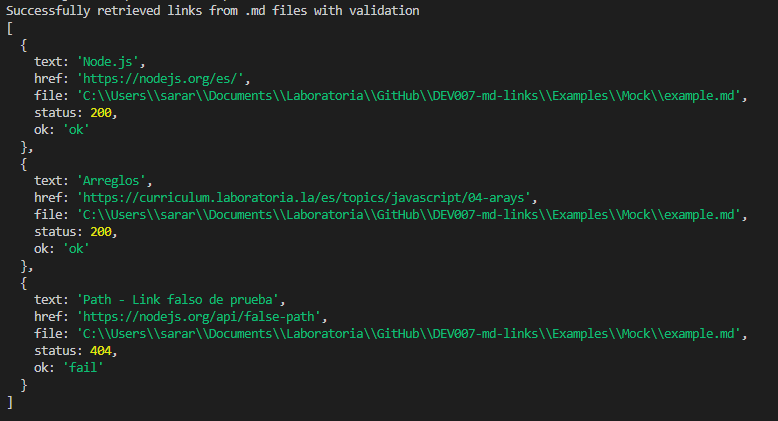
Only --validate: if only the --validate option is entered, the application will show you all the links found and will check if they are valid through an HTTP request. The status code and a message of ok/fail will be added to each link. If the path is not valid, or no .md file is found and error will appear.
npx @sara-rioseco/md-links <path> --validate
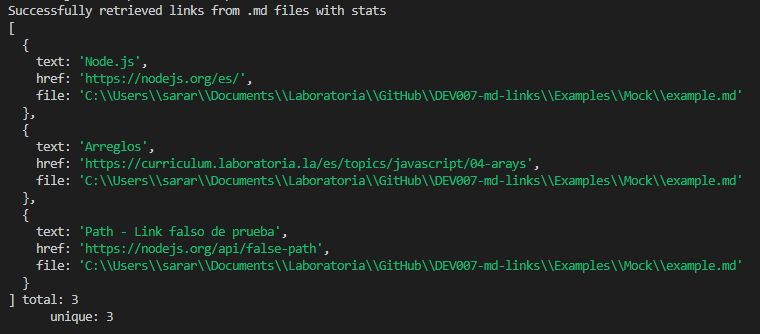
Only --stats: if only the --stats option is entered, the application will show you all the links found and will add a message with the total links found, and how many of them are unique links (the ones that are not repeated). If the path is not valid, or no .md file is found and error will appear.
npx @sara-rioseco/md-links <path> --stats
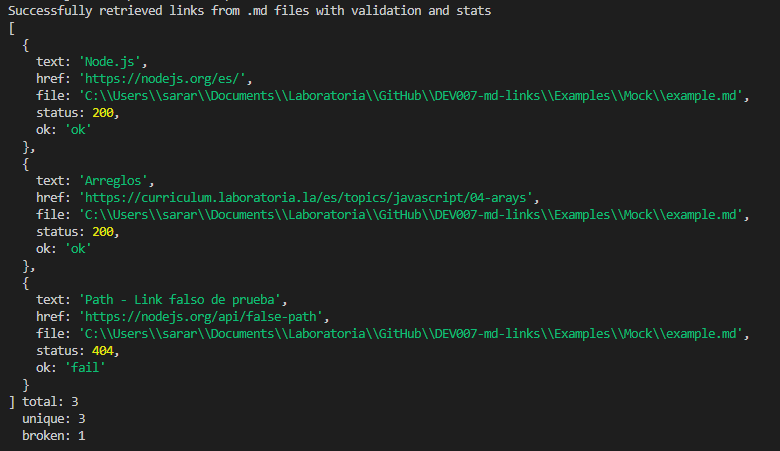
--validate and --stats: if the --validate and --stats options are provided, the application will show you all the links found and will check if they are valid through an HTTP request. The status code and a message of ok/fail will be added to each link. Also, a message will be added at te end saying the total amount of links found, how many of them are unique links (the ones that are not repeated) and how many are broken. If the path is not valid, or no .md file is found and error will appear.
npx @sara-rioseco/md-links <path> --validate --stats
As an API (Application Programming Interface)
Installation
In order to use the library as an API, follow these steps:
Fork the GitHub Repository.
Open your terminal and use the cd command to go to the folder where you want to save the project.
Run the following command:
git clone https://github.com/sara-rioseco/DEV007-md-links.gitOpen the folder you chose on your code editor software.
Open the terminal and you can start using the API.
How to use
Run the following command in your terminal:
node cli.js <path> [options]Where path is the route to the file or directory (it can be an absolute or relative path), and options are the additional actions you want to perform. Options are non mandatory, and the application will still run if only a path is provided. Possible options are: --validate, --stats, or both.
Expected output
No options: if no options are entered , the application will show you all the links found in that path. If the path is not valid, or no .md file is found and error will appear.
node cli.js <path>
Only --validate: if only the --validate option is entered, the application will show you all the links found and will check if they are valid through an HTTP request. The status code and a message of ok/fail will be added to each link. If the path is not valid, or no .md file is found and error will appear.
node cli.js <path> --validate
Only --stats: if only the --stats option is entered, the application will show you all the links found and will add a message with the total links found, and how many of them are unique links (the ones that are not repeated). If the path is not valid, or no .md file is found and error will appear.
node cli.js <path> --stats
--validate and --stats: if the --validate and --stats options are provided, the application will show you all the links found and will check if they are valid through an HTTP request. The status code and a message of ok/fail will be added to each link. Also, a message will be added at te end saying the total amount of links found, how many of them are unique links (the ones that are not repeated) and how many are broken. If the path is not valid, or no .md file is found and error will appear.
node cli.js <path> --validate --stats
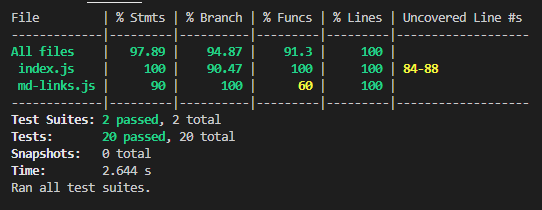
4. Unit tests with Jest 🤡
Unit tests were run using Jest, achieving a 97.89% of statements, 94.87% of branches, 91.3% of functions and 100% of lines, considering both files tested. You can check the results below:
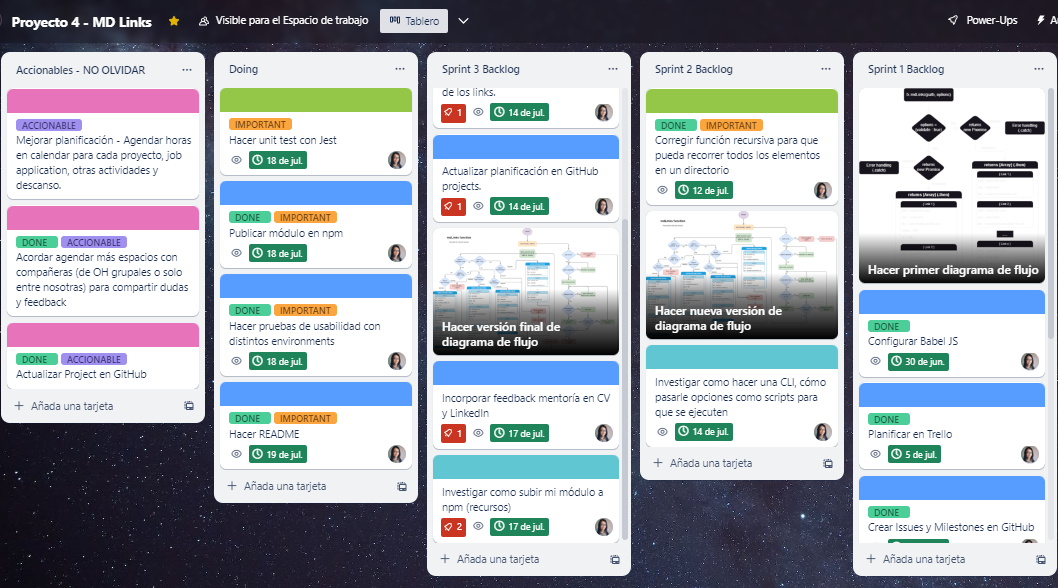
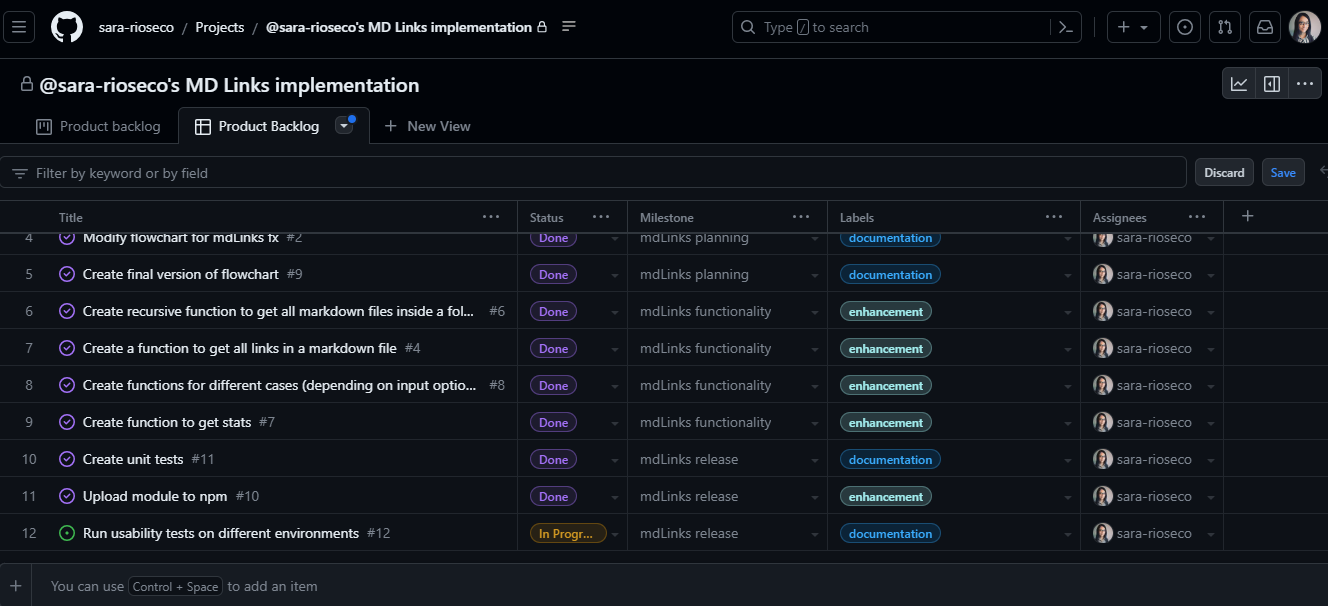
5. Planning 📆
For the planning of this project, I used the Trello app and also GitHub Projects, Issues, Milestones and Boards. You can find an image of both tools below.
Also during this stage, I designed a flowchart of the main function of the project. There were at least 3 different versions of this flowchart, you can see the final version below.
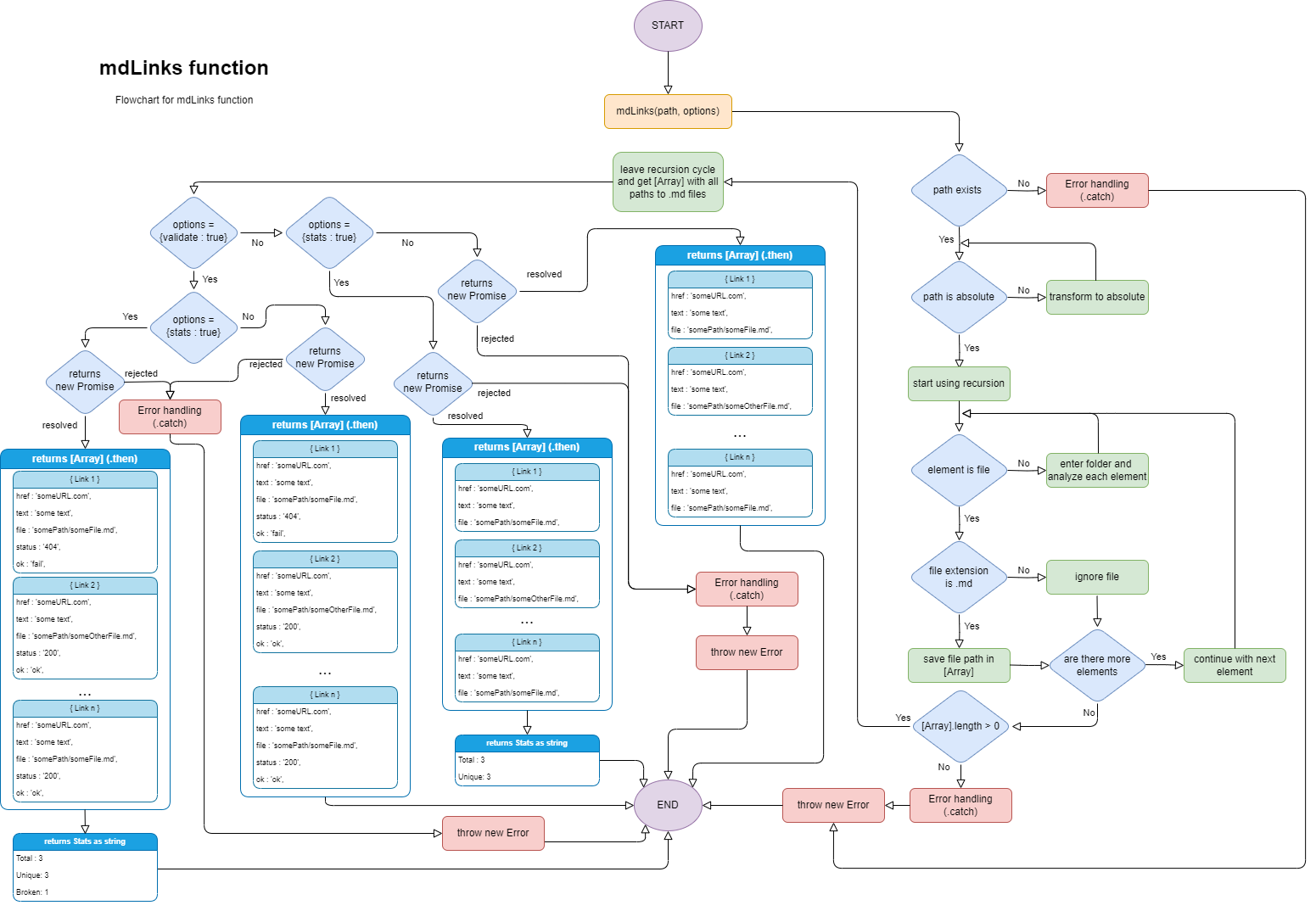
6. Requirements checklist ✔️
General
- [x] Can be installed with
npm install --global <github-user>/md-links
README.md
- [x] Backlog board for the implementation.
- [x] Technical documentation.
- [x] Installation and usage guide.
API mdLinks(path, opts)
- [x] The module exports a function with the expected API.
- [x] Individual file support implementation
- [x] Folder support implementation
- [x] Implementation of
options.validate
CLI
- [x] Displays excutable
md-linksin the path (added inpackage.json) - [x] It runs without errors / with the expected output
- [x] Implementation of
--validate - [x] Implementation of
--stats
Tests
- [x] Unit test coverage of at least 70% of statements, functions, lines and branches.
- [x] Tests passed (including linters) (
npm test).
7. Tools and skills 🛠️
JavaScript
- [x] Difference between primitive and non-primitive data structures
- [x] Arrays
- [x] Objects (key, value)
- [x] Conditionals (if-else, switch, ternary operator, boolean logic)
- [x] Functions (params, args, return)
- [x] Recursion
- [x] CommonJS Modules/ES Modules
- [x] Difference between expressions and statements
- [x] Callbacks
- [x] Promises
- [x] Unit tests
- [x] Asynchronous tests
- [x] Mocks and spies
- [x] Compatibility tests in different environments
- [x] Usage of linter (ESLINT)
- [x] Usage of descriptive identifiers (naming conventions and semantics)
Node.js
- [x] Installation and usage of npm modules
- [x] Package.json setup
- [x] Npm-scripts setup
- [x] process (env, argv, stdin-stdout-stderr, exit-code)
- [x] File system (fs, path)
Version Control (Git and GitHub)
- [x] Git: Installation and setup
- [x] Git: Version control (init, clone, add, commit, status, push, pull, remote)
- [x] Git: Branching and integration (branch, checkout, fetch, merge, reset, rebase, tag)
- [x] GitHub: Sign up, create a repository, add a SSH key
- [x] GitHub: Collaboration (branches | forks | pull requests | code review | tags)
- [x] GitHub: Organization (projects | issues | labels | milestones | releases)
HTTP
- [x] Request and response.
- [x] HTTP status codes