@priestine/versions
v1.13.1
Published
A tool for automating Semantic Versioning on your project
Downloads
49
Maintainers
Readme
||l
A tool for automating Semantic Versioning on your project.
Check out the roadmap for the project.
🔑 Table of Contents
✨ Features
- ✅ Compatible with GitHub releases. GitLab releases and direct git tagging (hello, BitBucket) on the way!
- ⚙️ Bump versions for the code written in any programming language with no configuration - only git matters
- 📝 Automatically generated list of changes that is put into the release body. An option to also write to a file will also be available!
- 🤔 Works with gitmoji commits convention, but you can configure it to your heart's content (see Conventions).
🏁 Getting Started
Using @priestine/versions is quite simple. You need Node installed and with that in place, you just npx @priestine/versions. Take a look at the examples provided below.
Local Machine Example
Go to the folder where your project lives and:
npx @priestine/versions --token=$TOKEN --repository=$OWNER/$REPOGitHub Actions Example
# The name may be anything you like
name: Priestine Versioning
on:
push:
# The workflow will run when a push lands on the master branch
branches: [master]
jobs:
# This name may also be arbitrary
versioning:
# I didn't test it on Windows but it should be ok
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
# Use checkout action to get the code
- uses: actions/checkout@v2
with:
# Full depth is important because by default checkout action only fetches one commit
fetch-depth: 0
# Install Node to make @priestine/versions work
- name: Setup Node
uses: actions/setup-node@v1
with:
node-version: '12.x'
# Do stuff
- name: Publish new version if applicable
run: npx @priestine/versions --token=${{ secrets.PRIESTINE_VERSIONS_TOKEN }} --repository=$GITHUB_REPOSITORY📝 Docs
Common
JavaScript
⚙️ Configuration
The provided configuration means have the following precedence:
- Configuration files are checked first and provided values replace defaults
- Environment variables are checked second and provided values replace defaults and configuration file values
- CLI options are checked last and provided values replace defaults, configuration file values and enviroment variable values
All options that accept true or false as a value are false by default.
Overview
| Option | CLI Usage Example | Environment Usage Example | Default |
| ----------------------------------------- | -------------------------------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------ | --------- |
| Config File | --config-file=PATH | PRIESTINE_VERSIONS_CONFIG_FILE=PATH | "" |
| Token | --token=$SOME_TOKEN | PRIESTINE_VERSIONS_TOKEN=$SOME_TOKEN | "" |
| Repository | --repository=octocat/github | PRIESTINE_VERSIONS_REPOSITORY=octocat/github | "" |
| Latest Version | --latest-version=0.0.0 | PRIESTINE_VERSIONS_LATEST_VERSION=0.0.0 | "" |
| Prefix | --prefix=v | PRIESTINE_VERSIONS_PREFIX=v | "" |
| Pre-Release | --pre-release=$(git rev-parse HEAD) | PRIESTINE_VERSIONS_PRE_RELEAS=$(git rev-parse HEAD) | "" |
| Build Metadata | --build-metadata=$(date) | PRIESTINE_VERSIONS_BUILD_METADATA=$(date) | "" |
| Custom URL | --custom-url=https://api.mygh.com/repos/ | PRIESTINE_VERSIONS_CUSTOM_URL=https://api.mygh.com/repos | "" |
| Merges | --merges=<include | exclude | only> | PRIESTINE_VERSIONS_MERGES=<include | exclude | only> | exclude |
| Bump Patch | --bump-patch[=<true | false>] | PRIESTINE_VERSIONS_BUMP_PATCH=<true | false> | false |
| Bump Minor | --bump-minor[=<true | false>] | PRIESTINE_VERSIONS_BUMP_MINOR=<true | false> | false |
| Bump Major | --bump-patch[=<true | false>] | PRIESTINE_VERSIONS_BUMP_MAJOR=<true | false> | false |
| Public | --public[=<true | false>] | PRIESTINE_VERSIONS_PUBLIC=<true | false> | false |
| Prefix Reset | --prefix-reset[=<true | false>] | PRIESTINE_VERSIONS_PREFIX_RESET=<true | false> | false |
| No Trailing Zeroes | --no-trailing-zeroes[=<true | false>] | PRIESTINE_VERSIONS_NO_TRAILING_ZEROES=<true | false> | false |
| Dry Run | --dry-run[=<true | false>] | PRIESTINE_VERSIONS_DRY_RUN=<true | false> | false |
| Show Changelog | --show-changelog[=<true | false>] | PRIESTINE_VERSIONS_SHOW_CHANGELOG=[=<true | false>] | false |
With CLI options that accept boolean values, providing those values is optional.
--bump-patchand--bump-patch=trueare completely the same.With environment variables that accept boolean values, providing those values is required.
Detailed description
Config File
You can provide a custom config file that contains application setup. Supported file formats are JSON, YAML and TOML. The files are allowed to provide any of the configuration for the app, including additional options that cannot be provided by other means.
Token
Token is used to publish the tag with associated release using GitHub API. For some reason, the $GITHUB_TOKEN that is automatically provided by GitHub Actions didn't work for me. So, for now, a custom token is needed. To make it work, you can just issue a token yourself. The token needs read/write access to the repository.
Repository
You MUST provide --repository=$REPOSITORY option that is usually available in CI tools already, e.g. $GITHUB_REPOSITORY in GitHub Actions. Internally, it is a part of the repository URL containing the owner and the repo name, e.g. priestine/versions for the @priestine/versions repository. Even if your CI tool doesn't provide it, it's not too complicated so you can put it yourself.
Latest Version
You can customize the tag from which @priestine/versions should start checking commits. NOTE - in this case, the version that will be produced by @priestine/versions may already be in place. Use carefully.
Prefix
Allows prefixing versions with things like v (e.g., v1.0.0). This is a common pattern as it enables easier glob matching for tags, but keep in mind that using a prefix makes the version non-compliant with Semantic Versioning.
Pre-Release
Allows setting SemVer pre-releases, e.g. rc or alpha. Do not add - at the beginning. @priestine/versions adds .1 at the end of the pre-release. If you specify --pre-release=rc, the pre-release on the version will look like -rc.1. @priestine/versions automatically checks if there is a pair of the same X.Y.Z version and pre-release. If it does exist, @priestine/versions automatically bumps the number at the end (-rc.1 -> -rc.2). This is done to prevent potential clashes in versions from different sources that represent candidates with the same potential version and pre-release.
Build Metadata
You can specify custom build metadata that will be appended to the version. Do not add the + at the beginning. @priestine/versions does not apply any modifications to build metadata so it is your responsibility to ensure their uniqueness.
Custom URL
You can specify custom URL of the API where the release should be published. This is useful for on-premise.
Merges
This option configures the usage of merge commits. If you want to use merge commits as the main source information about codebase changes, you may set up this option to only to avoid evaluating other commits. By default, merge commits are excluded.
Bump Patch
If, for some reason, you want to force bumping the patch version, even if it is not needed based on the types of commits you've made since the previous release, you can provide the --bump-patch. Keep in mind that this may negatively affect the appearance of your changelog.
Bump Minor
If, for some reason, you want to force bumping the minor version, even if it is not needed based on the types of commits you've made since the previous release, you can provide the --bump-minor. Keep in mind that this may negatively affect the appearance of your changelog.
Bump Major
If, for some reason, you want to force bumping the major version, even if it is not needed based on the types of commits you've made since the previous release, you can provide the --bump-major. Keep in mind that this may negatively affect the appearance of your changelog.
Public
According to the Semantic Versioning specification, releases that have a MAJOR version of 0 are not considered stable. Breaking changes for these releases bump MINOR version instead of the MAJOR one. These rules also apply if you use @priestine/versions - by default, your versions will have MAJOR version of 0. The changelog is created with MAJOR changes separate from MINOR ones, though. You can provide this option to exit the experimental stage. The closest release will be 1.0.0, thus declaring public API.
Applying this option is irreversible. This option is only applicable if you don't have releases with MAJOR version higher than 0. Otherwise, your project is considered to have public API declared already and you cannot publish 0.x.x versions anymore.
Prefix Reset
Setting this option to true will reset major version to 1 if the prefix changes. This option does not affect the versioning process if prefix is not provided. This option requires declaring public API. If major version was 0, this option will force it to be set to 1.
No Trailing Zeroes
Remove trailing zeroes in the new version, e.g. 14.0.0 -> 14 or 10.15.0 -> 10.15. NOTE: this is not compliant with Semantic Versioning. This option may be useful for creating new versions under the scheme Apple uses for their software. Alternatively, it can be applied to prettify CalVer-like versions.
Dry Run
Execute the command but skip publishing the release. May be useful for debugging or just to check what version your application is going to have next.
Show Changelog
Provide this option to include changelog in the console output. It is disabled by default as it may take quite a lot of space. This option can be helpful when setting up conventions, checking for commit message misspeling or commit type errors, or just to be able to say what you did yesterday during the daily scrum.
Conventions
Conventions can only be set up in config files. The conventions outline the process of finding commit types, binding those types to SemVer versions (major, minor or patch) and specify how the changes should be displayed in the change log. It is an array of objects of the following type:
/**
* Convention for defining how to get commit type, what version this
* type should bump, and how to display the change in the change log.
*/
export interface IConvention {
/**
* An array of strings containing RegExp that is used to check commit
* descriptions.
*/
match: string[]
/**
* Title for the group of commits of this type in the changelog.
*/
groupTitleFormat: string
/**
* Optional description for the group.
*/
groupDescription: string
/**
* A template describing how the commits of this type should be
* displayed in the changelog. Here you can use the following
* placeholders that will be replaced with the actual contents of the
* commit:
*
* - %commit.type%
* - %commit.description%
* - %commit.author.name%
* - %commit.author.email%
* - %commit.abbrevHash%
* - %commit.hash%
*/
itemDescriptionFormat: string
/**
* A template describing how the body of commits of this type should
* be displayed in the changelog (if it exists). Here you can use the
* %commit.body% placeholder that will be replaced with the actual
* contents of the commit body.
*/
itemBodyFormat: string
/**
* Semantic Version part that must be bumped if a commit of this type
* is found since previous version.
*/
bumps: 'patch' | 'minor' | 'major' | null
}NOTE that @priestine/semantics only adds line breaks (\n) between commits within a group.
You can see the default configuration for @priestine/versions below in the examples for config files.
Config Files
The files must have appropriate extensions:
.jsonfor JSON.ymlor.yamlfor YAML.tomlfor TOML
Config files allow deeper configuration than env variables and CLI options. Specifically, config files allow provision of conventions.
Here is a JSON example with the default settings for @priestine/versions. You can do the same with YAML and TOML as well.
{
"token": "",
"repository": "",
"latestVersion": "",
"prefix": "",
"preRelease": "",
"buildMetadata": "",
"customUrl": "",
"merges": "exclude",
"bumpPatch": false,
"bumpMinor": false,
"bumpMajor": false,
"public": false,
"prefixReset": false,
"noTrailingZeroes": false,
"dryRun": false,
"showChangelog": false,
"conventions": [
{
"match": ["^:ambulance:", "^:bug:", "^:lock:"],
"bumps": "patch",
"groupTitleFormat": "\n\n## :bug: ∘ :ambulance: ∘ :lock: Fixes\n",
"groupDescription": "",
"itemDescriptionFormat": "- %commit.description% (%commit.abbrevHash%)",
"itemBodyFormat": "> %commit.body%\n",
},
{
"match": ["^:sparkles:"],
"bumps": "minor",
"groupTitleFormat": "\n\n## :sparkles: Features\n",
"groupDescription": "",
"itemDescriptionFormat": "- %commit.description% (%commit.abbrevHash%)",
"itemBodyFormat": "> %commit.body%\n",
},
{
"match": ["^:boom:"],
"bumps": "major",
"groupTitleFormat": "\n\n## :boom: Breaking Changes\n",
"groupDescription": "",
"itemDescriptionFormat": "- %commit.description% (%commit.abbrevHash%)",
"itemBodyFormat": "> %commit.body%\n",
}
]🗺 How it works
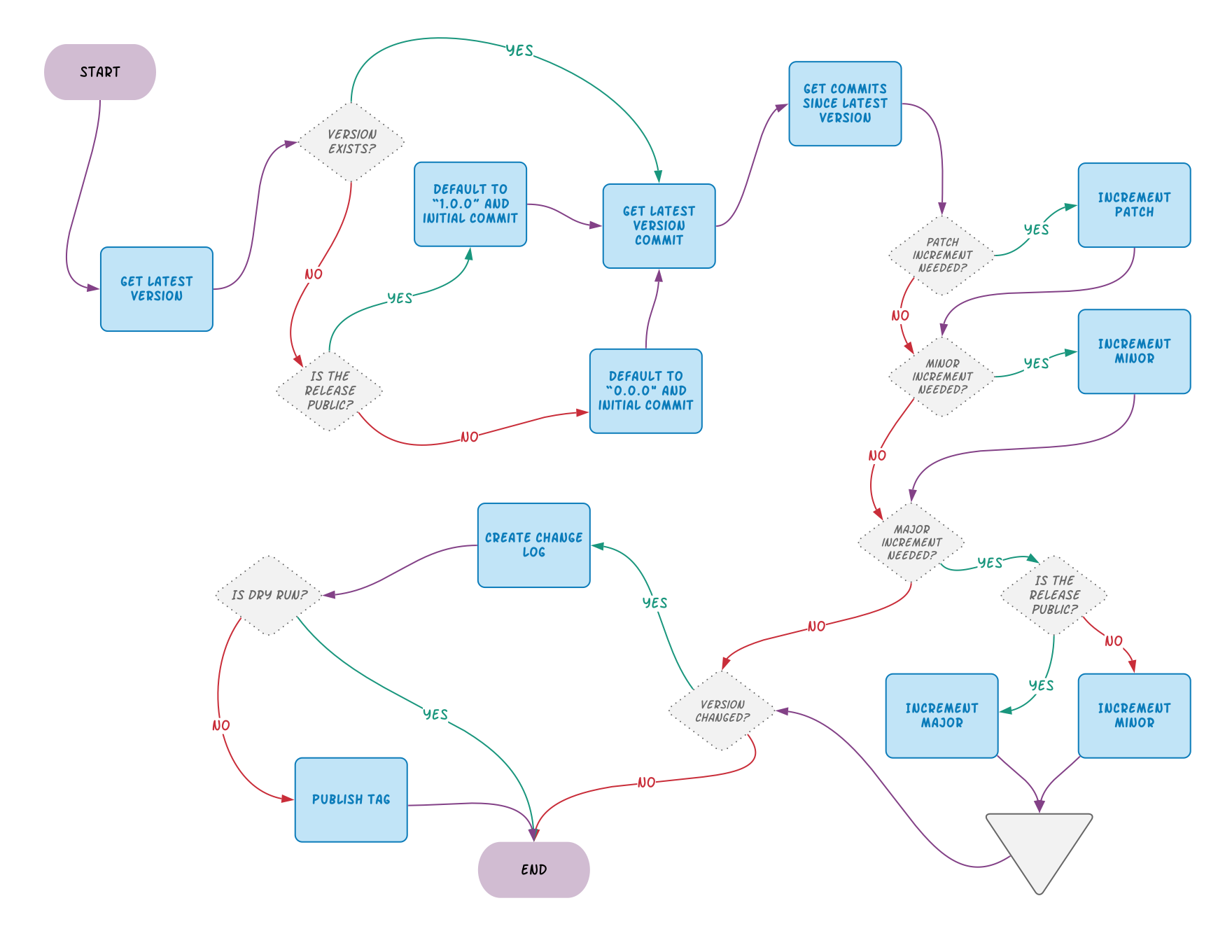
This intentionally over-complicated diagram depicts the application execution process:
🚫 Caveats
- Help needed - for some reason,
$GITHUB_TOKENdid not work for me when I tried to use it for creating releases from GitHub Actions. I am not very skilled with this tool so there's probably me doing something wrong. - Currently, @priestine/versions only works with GitHub (on-premise solutions not supported yet) and gitmoji as a commit convention.
- There might be a problem with using @priestine/versions with git repositories that have multiple unrelated histories merged. Specifically, when there are no previous Semantic Version tags and the tool tries to check commits since the initial commit. The problem is that in this case there will be multiple initial commits. Current workaround is to manually tag the commit that is desired to be used as the initial one, with a tag like '0.0.0' and then execute @priestine/semantics with
--latest-version=0.0.0.



