@patarapolw/furigana-markdown-it
v1.0.5
Published
Furigana extension for markdown-it.
Downloads
3
Maintainers
Readme
@patarapolw/furigana-markdown-it
A markdown-it plugin which adds furigana support.
If Furigana doesn't render on npm, try github instead.
Forked from https://github.com/iltrof/furigana-markdown-it.
TOC
Setup
Install via npm:
npm install @patarapolw/furigana-markdown-itUse with markdown-it:
const furigana = require("@patarapolw/furigana-markdown-it")();
const md = require("markdown-it")().use(furigana);
const html = md.render("[猫]{ねこ}");
// html == <p><ruby>猫<rp>【</rp><rt>ねこ</rt><rp>】</rp></ruby></p>Provide some options if you need (described below):
const furigana = require("@patarapolw/furigana-markdown-it")({
fallbackParens: "()",
extraSeparators: "-",
extraCombinators: "'",
lang: "ja-JP"
});
...Quick usage
Works:
| Input | Result | As image |
| ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ |
| [漢字]{かんじ} | 漢字【かんじ】 Or, if <ruby> is unsupported: 漢字【かんじ】 |  |
|
|
| [漢字]{かん・じ} (allowed separator characters: "..。・||//", as well as any kind of space) | 漢【かん】字【じ】 Or, if <ruby> is unsupported: 漢【かん】字【じ】 |  |
|
|
| [取り返す]{とりかえす} | 取【と】り返【かえ】す |  |
|
|
| [可愛い犬]{かわいいいぬ} | 可愛【かわいい】い犬【ぬ】 (wrong match!) | 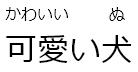 |
|
|
| [可愛い犬]{か・わい・いいぬ} | 可【か】愛【わい】い犬【いぬ】 |  |
|
|
| [可愛い犬]{か+わい・いいぬ} | 可愛【かわい】い犬【いぬ】 | 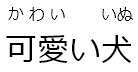 |
|
|
| [食べる]{たべる} | 食【た】べる |  |
|
|
| [食べる]{=たべる} | 食べる【たべる】 |  |
|
|
| [アクセラレータ]{accelerator} | アクセラレータ【accelerator】 |  |
|
|
| [accelerator]{アクセラレータ} | accelerator【アクセラレータ】 |  |
|
|
| [あいうえお]{*} (or {*}) | あ●い●う●え●お● |  |
|
|
| [あいうえお]{*❤} (or {*❤}) | あ❤い❤う❤え❤お❤ |  |
|
Doesn't work 😞:
- Formatting:
[**漢字**]{かんじ}doesn't make 漢字 bold. - Matching katakana with hiragana:
[バカな奴]{ばかなやつ}won't recognize that バカ and ばか are the same thing. - Matching punctuation (or any other symbols):
[「はい」と言った]{「はい」といった}will break on the 「」 brackets.
Not so quick usage
The basic syntax is [kanji]{furigana}, which results in
a <ruby> tag, with the kanji part being the main
content of the ruby, and the furigana part being the
annotation.
In other words, [漢字]{かんじ} turns into
漢字【かんじ】.
The plugin also generates fallback parentheses for
contexts where <ruby> tags happen to be unsupported. So
a browser that doesn't know about <ruby> tags would
display [漢字]{かんじ} as 漢字【かんじ】. The parentheses used can be
changed with the fallbackParens option when
initializing the plugin.
Annotating each kanji separately would be annoying, so
the plugin is also able to handle mixed kanji and kana.
For example, [取り返す]{とりかえす} correctly becomes
取【と】り返【かえ】す.
In a browser without <ruby> support it would look like
取【と】り返【かえ】す.
When relying on the above functionality, please keep in
mind that hiragana and katakana are treated separately.
So something like [バカな奴]{ばかなやつ} wouldn't work, and
neither would [ばかな奴]{バカなやつ}, because the plugin doesn't
consider ばか and バカ to be the same.
In some cases there's no unambiguous way to match
furigana to its kanji. Consider [可愛い犬]{かわいいいぬ}. Here
the plugin naively assigns かわいい to 可愛, and ぬ to 犬. The
desired result, however, is to have かわい assigned to 可愛,
and いぬ to 犬.
To resolve such ambiguities it's possible to indicate
where the kanji boundaries should be, like this:
[可愛い犬]{か・わい・いいぬ}. This is enough to leave us with only
one possible configuration:
可【か】愛【わい】い犬【いぬ】.
To indicate kanji boundaries you can use any space
character, as well as the following: "..。・||//". To use
other characters for this purpose, specify them in the
extraSeparators option when initializing the plugin.
Nonetheless, [可愛い犬]{か・わい・いいぬ} leaves us with another
problem. We were forced to separately annotate 可 with か,
and 愛 with わい. Instead it would be preferable to have 可愛
as a single entity with the furigana かわい. However, the ・
dot between か and わい is required to resolve the
ambiguity.
The solution to this problem is to use a + plus instead
of a ・ dot, like this: [可愛い犬]{か+わい・いいぬ}. This still
indicated that there is a kanji boundary between か and
わい, but tells the plugin not to separate 可愛 in the final
result:
可愛【かわい】い犬【いぬ】.
Instead of the ASCII plus (+) you can also use a full-width
plus (+). If you need any other characters to act as these
pluses, specify them in the extraCombinators option
when initializing the plugin.
If you feel so inclined, you can also let the plugin
match entire sentences:
[お前は、もう死んでいる]{おまえはもうしんでいる} produces
お前【まえ】は、もう死【し】んでいる.
However, don't put any punctuation into the furigana
part.
Other than pure Japanese, you should also get reliable results out of:
- English annotations to kana:
[ネコ]{cat}becomes ネコ【cat】.[ねこ]{cat}becomes ねこ【cat】.
- English annotations to kanji (without kana):
[漢字]{kanji}becomes 漢字【kanji】- And even
[漢字]{kan・ji}becomes 漢【kan】字【ji】
- Japanese annotations to English:
- All of
[cat]{ねこ},[cat]{ネコ},[cat]{猫}work as you'd expect.
- All of
- English annotations to English:
[sorry]{not sorry}becomes sorry【not sorry】.
If you want to bypass furigana matching and just stick
the annotation on top of the text as-is, add an equals
sign after the opening curly brace. For example,
[食べる]{=たべる} produces
食べる【たべる】.
The above notation accepts both the ASCII equals sign (=) and the full-width equals sign (=).
Bonus time!
Ever wanted to spice up your Japanese sentences with
em●pha●sis● dots●?
Worry no more: [あいうえお]{*} will do just that:
あ●い●う●え●お●!
And if you don't like the default look, provide a custom
character (or several) after the asterisk, like this:
[あいうえお]{*+} (result:
あ+い+う+え+お+).
Of couse, the full-width asterisk (*) also works.
Options
Options can be provided during initialization of the plugin:
const furigana = require("@patarapolw/furigana-markdown-it")({
fallbackParens: "()",
extraSeparators: "-",
extraCombinators: "'",
lang: "ja-JP"
});Supported options:
fallbackParens: fallback parentheses to use in contexts where<ruby>tags are unavailable. By default the plugin uses 【】 for fallback, so[漢字]{かんじ}becomes 漢字【かんじ】 on a rare browser without<ruby>support.This option takes a string with the opening bracket followed by the closing bracket.
extraSeparators: separators are characters that allow you to split furigana between individual kanji (read the usage section). Any kind of space is a separator, as well as these characters: "..。・||//".If you want additional characters to act as separators, provide them with this option.
extraCombinators: combinators are characters that allow you to indicate a kanji boundary without actually splitting the furigana between these kanji (read the usage section).Default combinators are + and +. If you need additional combinator characters, provide them with this option.
lang: this attribute may help define a proper variant of the same unicode point, that are merged due to Han unification.For example, 誤解 (ja-JP, Japanese), 誤解 (zh-CN, Chinese), 誤解 (ko-KR, Korean) may all look differently.
By default, lang attribute is absent in
<ruby>tags. If you need force a certain locale (like "ja-JP" for Japanese), provide one with this option.
