@ngxs-labs/firestore-plugin
v18.0.3
Published
 [](https://badge.fury.io/js/%40ngxs-labs%2Ffirestore-plugin) [
Quick start
Install the plugin:
- npm
npm install --save @ngxs-labs/firestore-plugin- yarn
yarn add @ngxs-labs/firestore-pluginIn your app.module.ts include the plugin, you will also need to include @angular/fire and NgxsModule, as they are
peer dependencies for the plugin. Make sure also you have installed firebase library as well.
Firebase (Modular)
import { NgxsModule } from '@ngxs/store';
import { NgxsFirestoreModule } from '@ngxs-labs/firestore-plugin';
import { provideFirebaseApp, getApp, initializeApp } from '@angular/fire/app';
import { getFirestore, provideFirestore } from '@angular/fire/firestore';
@NgModule({
imports: [
provideFirebaseApp(() => initializeApp({ ... })),
provideFirestore(() => getFirestore()),
NgxsModule.forRoot(),
NgxsFirestoreModule.forRoot()
],
...
})
export class AppModule { }Firebase (Compat)
//...
import { NgxsModule } from '@ngxs/store';
import { NgxsFirestoreModule } from '@ngxs-labs/firestore-plugin/compat';
import { AngularFireModule } from '@angular/fire/compat';
import { AngularFirestoreModule } from '@angular/fire/compat/firestore';
@NgModule({
declarations: [AppComponent, ListComponent],
imports: [
//...
AngularFireModule.initializeApp(environment.firebase),
AngularFirestoreModule,
NgxsModule.forRoot(),
NgxsFirestoreModule.forRoot()
]
//...
})
export class AppModule {}Next create a service (i.e races.firestore.ts) to execute Firestore operations. This service extends NgxsFirestore,
a generic service that takes type <T> of the Firestore document. We also need to provide the path of the Firestore
collection.
//...
import { NgxsFirestore } from '@ngxs-labs/firestore-plugin';
// or if you are using firebase compat
import { NgxsFirestore } from '@ngxs-labs/firestore-plugin/compat';
@Injectable({
providedIn: 'root'
})
export class RacesFirestore extends NgxsFirestore<Race> {
protected path = 'races';
}Finally we create the @State. The state will contain actions to execute the Firestore CRUD operations via the service
created previously. When getting data from Firestore, we have two options:
- Get data once
- Connect to a document or collection stream and receive changes as they occur on the Firestore server.
Connect and get data once
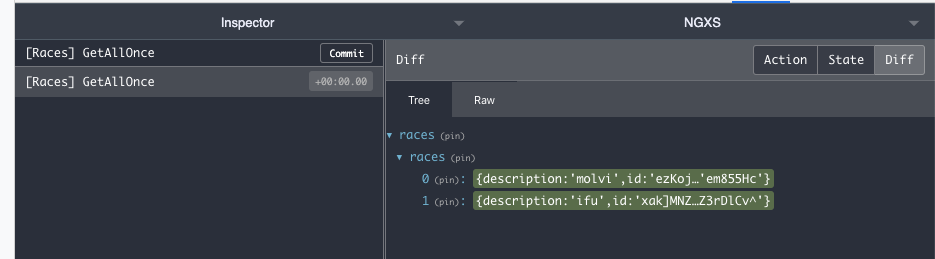
For the first scenario, NgxsFirestore provides the methods docOnce$() and collectionOnce$(), which will get the
first emission and unsubscribe immediately after. NGXS handles subscribing to the Observable and the action is done
once the first data is emmited.
export class GetAllOnce {
public static readonly type = '[Races] GetAllOnce';
}
@State<RacesStateModel>({
name: 'races',
defaults: {
races: []
}
})
export class RacesState {
constructor(private racesFS: RacesFirestore) {}
@Action(GetAllOnce)
getAllOnce({ getState, patchState }: StateContext<RacesStateModel>) {
return this.racesFS.collectionOnce$().pipe(
tap((races) => {
patchState({ races: races });
})
);
}
}
Connect to stream and receive data changes until disconnected
For the second scenario, the plugin provides the NgxsFirestoreConnect service, which let's you connect an @Action
with a Firestore query and emit every new change as a separate Emitted action.
The service connect method takes as arguments the Action that will trigger subscribing to the Firestore query. In
addition an opts object with to field, to pass the function that returns the Firestore query.
Once connection is setup, you can then create handlers for the specific events of the stream.
You can add handlers for:
Connected event with
@Action(StreamConnected(RacesActions.GetAll)).This event will be fired once on first emission.
Emmited event with
@Action(StreamEmitted(RacesActions.GetAll))This event will be fired each observable emission. This action will return
Emitted<Action, T>whereActionis the action bound, andTis the type of the returned results from the Firestore query.Disconnected event with
@Action(StreamDisconnected(RacesActions.GetAll))This event will be fired on observable disconnect.
//...
import { NgxsFirestoreConnect } from '@ngxs-labs/firestore-plugin';
export class GetAll {
public static readonly type = '[Races] GetAll';
}
export class Get {
public static readonly type = '[Races] Get';
constructor(public payload: string) {}
}
export class RacesState implements NgxsOnInit {
//...
constructor(private racesFS: RacesFirestore, private ngxsFirestoreConnect: NgxsFirestoreConnect) {}
ngxsOnInit() {
// query collection
this.ngxsFirestoreConnect.connect(RacesActions.GetAll, {
to: () => this.racesFS.collection$()
});
// query doc
this.ngxsFirestoreConnect.connect(RacesActions.Get, {
to: (action) => this.racesFS.doc$(action.payload),
trackBy: (action) => action.payload
});
}
// GetAll
@Action(StreamConnected(RacesActions.GetAll))
getAllConnected(ctx: StateContext<RacesStateModel>, { action }: Connected<RacesActions.GetAll>) {
// do something when connected
}
@Action(StreamEmitted(RacesActions.GetAll))
getAllEmitted(ctx: StateContext<RacesStateModel>, { action, payload }: Emitted<RacesActions.Get, Race[]>) {
ctx.setState(patch({ races: payload }));
}
@Action(StreamDisconnected(RacesActions.GetAll))
getAllDisconnected(ctx: StateContext<RacesStateModel>, { action }: Disconnected<RacesActions.GetAll>) {
// do something when disconnected
}
//Get
@Action(StreamEmitted(RacesActions.Get))
get(ctx: StateContext<RacesStateModel>, { action, payload }: Emitted<RacesActions.Get, Race>) {
ctx.setState(
patch({
races: iif(
(races) => !!races.find((race) => race.id === payload.id),
updateItem((race) => race.id === payload.id, patch(payload)),
insertItem(payload)
)
})
);
}
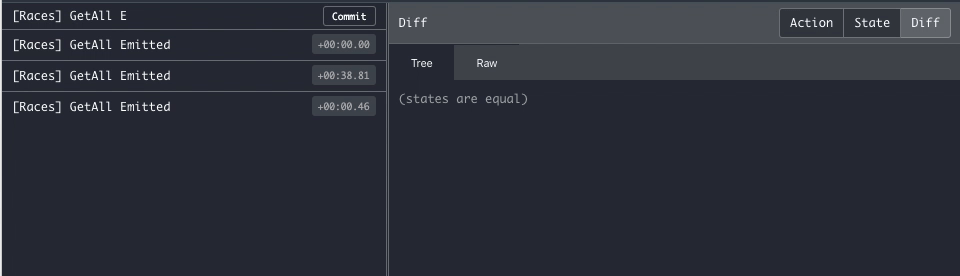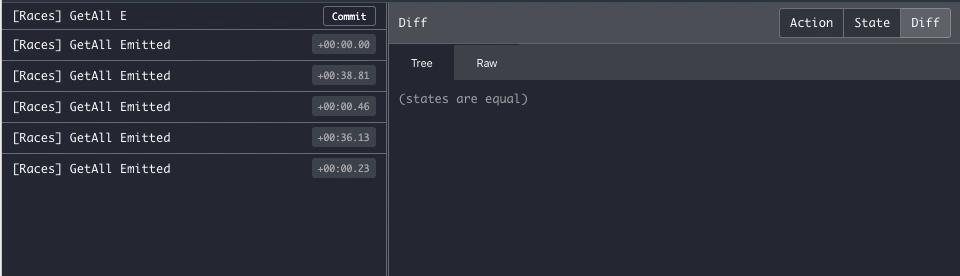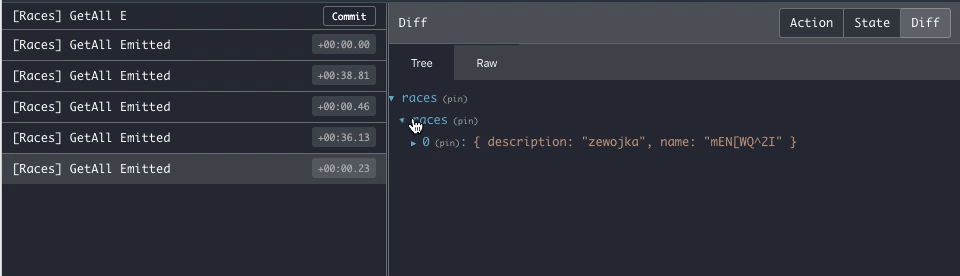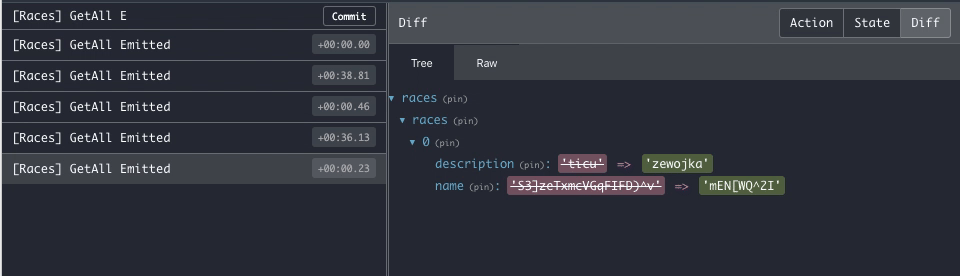
}Once you connect to the Firestore stream you'll keep receiving every server update on a new Emitted action, making it
easier to debug.
Adding write operations
When adding write operation to your state, you can use the helper methods from NgxsFirestore. Since your data is
connnected from Firestore, every write operation you run in the state will trigger an emission and update the state.
export class Create {
public static readonly type = '[Races] Create';
constructor(public payload: Race) {}
}
export class RacesState implements NgxsOnInit {
//...
// Create
@Action(RacesActions.Create)
create(ctx: StateContext<RacesStateModel>, { action }: Connected<RacesActions.Create>) {
// do something when connected
return this.racesFS.create$(action.payload);
}
}Getting data from Firestore and Disconnecting
After all your Firestore queries are bind to its respective Actions, you can start getting data by dispatching the
Action like this:
//...
this.store.dispatch(new RacesActions.GetAll());
// or
this.store.dispatch(new RacesActions.Get(id));If you need to disconnect you can dispatch
//...
this.store.dispatch(new Disconnect(new RacesActions.GetAll()));
// or
this.store.dispatch(new Disconnect(new RacesActions.Get(id)));NgxsFirestore options
NgxsFirestore allows to setup an "id" field, and automatically set the Firestore's doc id in the response object. To do
this, you just need to setup idField in your NgxsFirestore class.
export class RacesFirestore extends NgxsFirestore<Race> {
idField = 'raceId';
}Another option you can setup is a conversion on items that come from or go to Firestore. You can do this, setting a
firebase.firestore.FirestoreDataConverter and configure toFirestore and fromFirestore. toFirestore will be
applied before saving the object to Firestore and fromFirestore will be applied when items are streamed from Firestore
to your app.
export class RacesFirestore extends NgxsFirestore<Race> {
protected path = 'races';
idField = 'raceId';
converter: firebase.firestore.FirestoreDataConverter<Race> = {
toFirestore: (value) => {
const db = { ...value };
delete db.testProp;
return db;
},
fromFirestore: (snapshot, options) => {
const data = snapshot.data(options);
return <Race>{ ...data, testProp: data.id + data.title };
}
};
}You can also configure if you want to retrieve the metadata from firestore document.
Enabling fetching metadata, you will get fromCache and hasPendingWrites fields that can be useful to inform users if
data is being read from the server or writes have already been commited to the database.
You can disable metadata setting it to false.
export class RacesFirestore extends NgxsFirestore<Race> {
metadataField = '_metadata';
}Retrieving data from subcollections
When you need to pull data from a subcollection you can create a specific Firestore service for the subcollection. Let's say the races collection, contains a classification subcollection, then you could setup the Firestore subcollection service like this.
@Injectable({
providedIn: 'root'
})
export class ClassificationsFirestore extends NgxsFirestore<Race> {
protected get path() {
return `races/${this.raceId}/classifications`;
}
private _raceId = '';
public setRaceId(raceId) {
this._raceId = raceId;
}
protected get raceId() {
return this._raceId;
}
}Paging
Firestore allows us to page queries using a combination of limit and startAt options when we create our query. This
plugin includes a simple approach to allow fetching from the database using limit.
//...
constructor(
//...
private ngxsFirestoreConnect: NgxsFirestoreConnect,
private ngxsFirestorePage: NgxsFirestorePageService
) {}
ngxsOnInit(ctx: StateContext<RacesStateModel>) {
this.ngxsFirestoreConnect.connect(GetPages, {
to: () => {
const obs$ = this.ngxsFirestorePage.create((pageFn) => this.racesFS.collection$((ref) => pageFn(ref)), 5, [
{ fieldPath: 'title' }
]);
return obs$;
}
});
}
In your @State you include the NgxsFirestorePageService that we'll use to connect the paged query with NGXS. The
page service will create a managed Observable based on the query you pass into. You completed the configuration with
the page size and the fields to order the query by.
The page service will fetch first page when you dispatch the connected @Action, in the example GetPages, and will
increase the fetched results on each subsequent GetNextPage. The result will be 5 items pulled initially, 10 items
after GetNextPage and so on and so forth. This way you always get synced results with the database and increase the
size when you need to see more items. Along with GetNextPage the plugin includes GetLastPage that will decrease the
size pulled when dispatched.
This approach does not support paging queries providing where to start getting results from, but it is a simple way to limit queries and still be connected with the NGXS store.
@angular/fire - firebase.js compatibility
In version 1.2.x the plugin will include two NgxsFirestore to allow compatibility with firebase compat and modular.
The service name will remain the same but the compat version will be exported under
@ngxs-labs/firestore-plugin/compat.
The compat submodule will also export NgxsFirestoreAdapter, NgxsFirestorePageService and
NgxsFirestorePageIdService.
If you intend to keep using compat version for a while, make sure you are using the correct import
@ngxs-labs/firestore-plugin/compat.
