@mahendrapaipuri/jupyter-power-usage
v1.1.1
Published
Extension that shows system power usage
Downloads
22
Maintainers
Readme
jupyter-power-usage

The objective of this extension is to display power usage of the CPU and/or GPU on which jupyter server is running. Power usage is estimated using Running Average Power Limit (RAPL) metrics that are available on Intel processors manufactured after 2012 (since broadwell). It is available on latest AMD processors as well. For the case of GPUs, currently only nVIDIA GPUs are supported and power usage is gathered from nvidia-smi tool.
Additionally, the extension is capable of estimating equivalent CO2 emissions. Emissions are estimated based on the current power usage and a emission factor that gives equivalent grams of CO2 power consumed. Currently, a real time emission factor is implemented for France and for the rest a constant configurable factor of 475 gCO2.eq/kWh is used.
The metrics are displayed in the top bar of JupyterLab and are updated at a configurable interval. The default interval is 5 seconds. RAPL can enforce power limit so as nVIDIA GPUs. If those power limits are enabled and available, they will be displayed in the indicators.
NOTE
The extension works only on Linux that exposes RAPL metrics. Starting from kernel 5.4, RAPL metrics are accessible only for root. In this case, the user needs to add read permissions on /sys/fs/powercap directory to be able to display power usage indicators in JupyterLab.
If the JupyterLab is running inside a container or VM, ensure that /sys/fs/powercap file system exists. If it does not, extension will not work.
The extension is not available for Notebook < 6. It supports JupyterLab >= 3 and Notebook >= 7.
The extension's architecture closes follows the jupyter-resource-usage extension and all the credit goes to the contributors and maintainers of the above stated extension.
Installation
JupyterLab 3.x
You should install the version <1.0.0 for JupyterLab 3.x compatibility.
pip install 'jupyter-power-usage<1.0.0'JupyterLab 4.x and Notebook 7.x
You should install the latest version for JupyterLab 4.x and Notebook 7.x compatibility.
pip install jupyter-power-usageThe extension does not support Notebook < 7.
Configuration
Server side config
Measurement Scope
Currently the extension supports different measurement scopes:
process: Power usage for current process and its children will be reporteduser: Power usage for current user processes will be reportedsystem: Power usage for entire system will be reported.
By default process scope is used. The user can change it by CLI flag --PowerUsageDisplay.measurement_scope to jupyter lab command. Alternatively, it can be configured in jupyter_server_config.json in Jupyter config directory.
Electricity Maps API token
An API token for electricity maps emission factor. By default API requests are made from jupyter server as they involve including authentication token. These are called proxied requests. If they fail, API requests directly from the browser will be made using the API token configured in the frontend extension. Users should configure the token on the server config as exposing API token in browsers can pose security issues. It can be set on CLI using --PowerUsageDisplay.emaps_access_token=<token>.
Frontend extension config
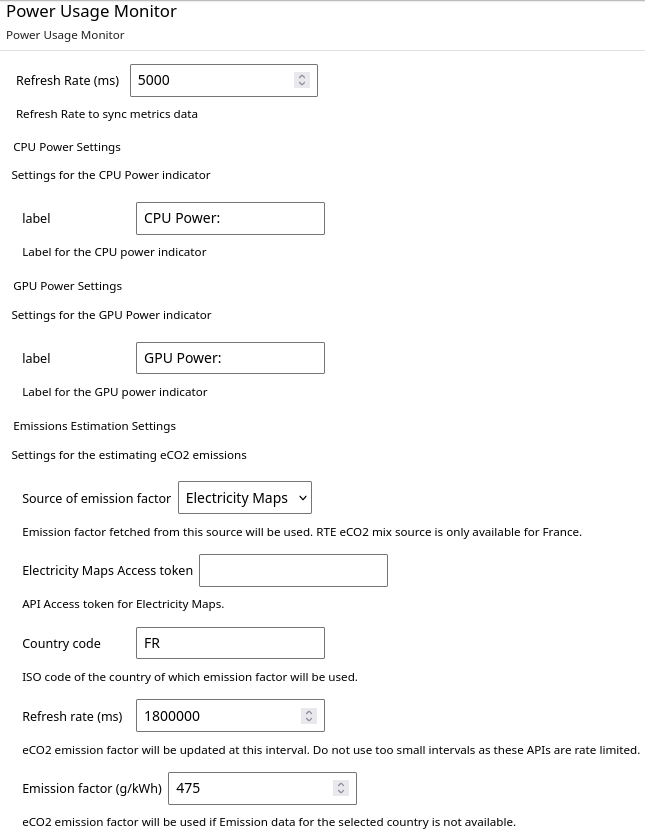
The frontend extension settings can be accessed by Settings -> Advanced Settings -> Power Usage Monitor in JupyterLab. Important settings are:
Refresh Rate: Frequency at which power usage is updated in the JupyterLab. Do not use too small intervals as it will end up making too many API calls to update metrics.CPU labelandGPU labelsettings are self explanatory.
Emissions Estimation Settings
Source of emission factor: Currently Electricity Maps and RTE eCO2 mix are supported. Note that RTE eCO2 mix data is only available for France.Electricity Maps Access token: An API access token for Electricity Maps (See Server Config).Country code: ISO 3166-1 alpha-2 country code. This will be used only whenElectricity Mapsemission factor source is used.Refresh rate: This defines how often the emission factor is updated in ms. For RTE eCO2 mix data, it is updated every 30 min and has a rate limit of 50000 API requests per month.Emission factor: This constant emission factor is used in the estimation of emissions when country specific data is unavailable.
Contributing
If you would like to contribute to the project, please read the CONTRIBUTING.md. The CONTRIBUTING.md file
explains how to set up a development installation and how to run the test suite.
Uninstall
pip uninstall jupyter_power_usageThis will uninstall python package and all the frontend related assets.
Troubleshooting
If power indicators do not show up in the JupyterLab, try reload the browser tab. Sometimes network latencies prevent extension to load in time.
If there are any issues with the server side extension, they will be logged to the same log that JupyterLab uses.


