@feup-infolab/docker-mocha
v0.0.18
Published
Running mocha tests in isolated, parallel and cached environments
Downloads
3
Readme
Docker-Mocha
Service/end-to-end tests execution in local and isolated environment. With Setup Caching (Dissertation Nuno Neto)
Introduction
Docker-Mocha is a npm package developed in order to optimize a very characteristic set of test environments. Environments with a considerable ammount of service/end-to-end tests and with setup dependencies. In a normal execution these test suites would run in the host machine, single threaded and with multiple recreations of previous test setup states. The resulting unoptimized pipeline might provide undisired execution times.
Docker-Mocha solves this problem by using isolated docker environments with its own network. Each test will run in one of these docker environments. By having isolation, it is possible to run the whole suite in paralel. Additionaly, every setup state is saved (cached) in order for the sucessor test to load and execute more quickly.
These set of charactericstis allow to improve the overall execution time of the test suite.
Requirments
- Docker CE
- Node.js
- Netcat
- Linux or MacOS
Support
This module only supports mocha tests. No windows support is available either given the design architecture of docker in windows (see this).
Setup
To setup docker-mocha the users need to first verify that the requirments are met. Then install it via npm install @feup-infolab/docker-mocha. Additional setup steps are required as it follows:
Tests file
The users must create a tests.json file where they list all the setups and tests. Each setup and test must have a specific set of paramethers as well as a unique identifier string:
Additional paramethers for each setup
Parameter | Description
--------- | -----------
depends_on | Identifier of the parent state it deppends on. If root, leave it null
path | the relative path of the setup file, from the project root. It can be null
Additional paramethers for each test
Parameter | Description
--------- | -----------
state | Identifier of the state it deppends on. It cannot be null
path | the relative path of the test file, from the project root. It cannot be null
Example
{
"states":
{
"init": {"depends_on": null, "path": null},
"setDollar": {"depends_on": "init", "path": "setup/init.js"},
"setPound": {"depends_on": "init", "path": "setup/init.js"},
"testDollar": {"depends_on": "setDollar", "path": "setup/dollar/setDollar.js"},
"testPound": {"depends_on": "setPound", "path": "setup/pound/setPound.js"}
},
"tests":
{
"init": {"state": "init", "path": "test/init.js"},
"setDollar": {"state": "setDollar", "path": "test/dollar/setDollar.js"},
"setPound": {"state": "setPound", "path": "test/pound/setPound.js"},
"testDollar": {"state": "testDollar", "path": "test/dollar/testDollar.js"},
"testPound": {"state": "testPound", "path": "test/pound/testPound.js"}
}
}For each test, if the state for it does not exist, it will use the parent state, run the setup and execute the test. If the state already exists, then the setup will not be executed.
Compose file
This module makes heavy use of docker in order to work. Also, in order to isolate the test environment it requires a valid docker-compose.yml. Version 3.5 or above is required. The users will initially design the environment needed to mount the whole platform environment. If there is already a compose file for the platform, then the recommended is to create a copy only for docker-mocha. After creating or copying the file, the compose file must obey a set of rules and alterations:
- The
container_nameproperty for each service must exist. Also, the string${TEST_NAME}.should be attached at the beggining of the name string. - The
imageproperty for each service must exist. The users are welcome to use the tag they want to, as long as they use one. If the users are used to ignoring it, use thelatesttag. After the image tag the users must attach the string${PARENT_STATE}at the end. - The users must attach a network at the end of the compose file. That network must have a name
${TEST_NAME}and the driver must bebridge. - (optional) The users are welcome to use the build property with dockerfiles for custom projects in docker containers. As long as they follow rule number 2.
- (optional) If the users require for the containers to communicate with each other, then the typical
localhost:{port}will not work. For each service, they must add an alias for the network created in rule number 3.
Example
version: '3.5'
services:
dendro:
container_name: ${TEST_NAME}.dendro
image: nuno/node-currency:latest${PARENT_STATE}
build:
context: .
dockerfile: dockerfiles/Dockerfile
networks:
custom_net:
aliases:
- dendro
mongo:
container_name: ${TEST_NAME}.mongo
image: mongo:3${PARENT_STATE}
networks:
custom_net:
aliases:
- mongo
networks:
custom_net:
name: ${TEST_NAME}
driver: bridgeOptions
To run docker-mocha the users simply need to invoke docker-mocha in the project root. Aditional options are available
Argument | Alias | Type | Description | Default Value
--------- | ------| ---- | ----------- | -------------
--file | -f | string |The relative path to the tests file, relative to the project root. | tests.json
--compose | -c | string | The relative path to the docker compose file, relative to the project root. | docker-compose.yml
--threads | -t | int | The maximum ammount of tests running in parallel. | 4
--entrypoint | -e | string | The name of the services in which the tests will be executed. | project name in package.json
--port | -p | int | The port of the entrypoint service. The execution only continues when the entrypoint + port specified are up | 3000
--config | | string | A specificic config environment variable that it will be passed to the setup and tests in runtime | (undefined) |
Flags
Flag | Description
--------- | ------
--no-checkpoint | Does not use existing states. Creates base containers and runs all the setups till it reaches the current test
--no-delete | Does not delete all the existing states before the execution beggins
Example
docker-mocha -f ./test/tests.json -t 2 -c docker-compose.yml -e dendro -p 3000 --no-deleteTesting
These following tests are provided in this project which were used to debug the implementation of docker-mocha. To use this command please change directory to the sub-folder test: cd test
Running tests locally
- Run
npm test
Running tests inside docker compose
- Run
npm run test-docker
Running tests with docker-mocha
- Run
npm run docker-mocha
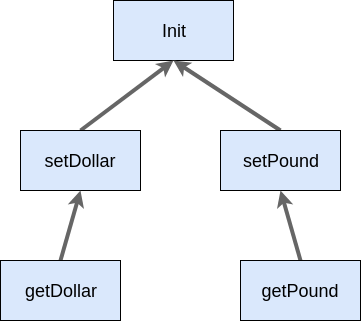
Current test approach and dependency tree