@dxfrontier/cds-ts-dispatcher
v4.0.1
Published
The goal of CDS-TS-Dispatcher is to significantly reduce the boilerplate code required to implement TS handlers provided by the SAP CAP framework.
Downloads
1,085
Maintainers
Readme











The goal of CDS-TS-Dispatcher is to significantly reduce the boilerplate code required to implement Typescript handlers provided by the SAP CAP framework.
Table of Contents
- Table of Contents
- Prerequisites
- Installation
- Usage
Deploymentto BTP using MTABest practices&tipsSamples- Contributing
- License
- Authors
Prerequisites
Install @sap/cds-dk, typescript, ts-node globally:
npm install -g @sap/cds-dk typescript ts-nodeInstallation
Option 1 : Install CDS-TS-Dispatcher - New project
Using: @sap/cds v8
Use the following steps if you want to create a new SAP CAP project.
- Create new folder :
mkdir project
cd project- Initialize the CDS folder structure :
cds init- Add
TypeScriptand CDS-Typer to your npm package.json:
cds add typescript- Add
CDS-TS-Dispatcherto your npm package.json :
npm install @dxfrontier/cds-ts-dispatcher- It is recommended to use the following tsconfig.json properties:
{
"compilerOptions": {
"esModuleInterop": true,
"skipLibCheck": true,
"allowJs": true,
"resolveJsonModule": true,
"isolatedModules": true,
"strictNullChecks": true,
"strictPropertyInitialization": false,
"forceConsistentCasingInFileNames": true,
"allowSyntheticDefaultImports": true,
"strict": true,
"experimentalDecorators": true,
"emitDecoratorMetadata": true,
"target": "ES2021",
"module": "NodeNext",
"moduleResolution": "NodeNext",
"outDir": "./gen/srv",
"rootDir": ".",
"paths": {
"#cds-models/*": ["./@cds-models/*/index.ts"]
}
},
"include": ["./srv", "./@dispatcher"]
}- Install packages
npm install- Run the
CDS-TSserver
cds-ts w[!IMPORTANT] CDS-TS-Dispatcher uses
@sap/cds,@sap/cds-dkversion 8
Using: @sap/cds v7
Use the following steps if you want to create a new SAP CAP project.
- Create new folder :
mkdir new-sap-cap-project
cd new-sap-cap-project- Initialize the CDS folder structure :
cds init- Add CDS-Typer to your npm package.json:
cds add typer
npm install- Add the the following NPM packages :
npm install @dxfrontier/cds-ts-dispatcher@2
npm install --save-dev @types/node- Add a tsconfig.json :
tsc --init- It is recommended to use the following tsconfig.json properties:
{
"compilerOptions": {
"esModuleInterop": true,
"skipLibCheck": true,
"allowJs": true,
"resolveJsonModule": true,
"isolatedModules": true,
"strictNullChecks": true,
"strictPropertyInitialization": false,
"forceConsistentCasingInFileNames": true,
"allowSyntheticDefaultImports": true,
"strict": true,
"experimentalDecorators": true,
"emitDecoratorMetadata": true,
"target": "ES2021",
"module": "NodeNext",
"moduleResolution": "NodeNext",
"outDir": "./gen/srv",
"rootDir": ".",
"paths": {
"#cds-models/*": ["./@cds-models/*/index.ts"]
}
},
"include": ["./srv", "./@dispatcher"]
}
- Run the
CDS-TSserver
cds-ts watchMigration: from @sap/cds v7 to v8
Use the following steps if you want to migrate from @sap/cds@7 to @sap/cds@8:
- Verify you've installed the
cds@v8globally by running the following command:
cds -v -i| packages | version |
| ---------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ |
| @cap-js/asyncapi | 1.0.1 |
| @cap-js/cds-typer | 0.24.0 |
| @cap-js/cds-types | 0.6.4 |
| @cap-js/openapi | 1.0.4 |
| @cap-js/sqlite | 1.7.3 |
| @sap/cds | 8.1.0 |
| @sap/cds-compiler | 5.1.2 |
| @sap/cds-dk (global) | 8.0.2 |
| @sap/cds-fiori | 1.2.7 |
| @sap/cds-foss | 5.0.1 |
| @sap/cds-lsp | 8.0.0 |
| @sap/cds-mtxs | 1.18.2 |
| @sap/eslint-plugin-cds | 3.0.4 |
| Node.js | v22.4.1 |
[!TIP] If you see a smaller version than
@sap/cds-dk (global)8.0.2run the following command :npm install -g @sap/cds-dk@latest
- Run the following command inside of your project:
cds add typescript[!TIP] Command above will add the following packages:
@types/node@cap-js/cds-types@cap-js/cds-typertypescript
- After running command above the
package.jsonwill look similar to :
{
"dependencies": {
"@dxfrontier/cds-ts-dispatcher": "^3.0.0",
"@dxfrontier/cds-ts-repository": "^1.1.3",
"@sap/cds": "^8.1.0",
"express": "^4.19.2"
},
"devDependencies": {
"@cap-js/sqlite": "^1.7.3",
"@cap-js/cds-types": "^0.6.4",
"typescript": "^5.5.4",
"@types/node": "^22.1.0",
"@cap-js/cds-typer": ">=0.24.0"
},
"scripts": {
"start": "cds-serve",
"watch": "cds-ts w",
},
}[!IMPORTANT] You might delete the
node_modulesfolder andpackage-lock.jsonin casenpm run watchfails working.Re-run the following command :
npm install
Option 2 : Install CDS-TS-Dispatcher - Existing project
Use the following steps if you want to add only the @dxfrontier/cds-ts-dispatcher to an existing project :
npm install @dxfrontier/cds-ts-dispatcherIt is recommended to use the following tsconfig.json properties:
{
"compilerOptions": {
/* Base Options: */
"esModuleInterop": true,
"skipLibCheck": true,
"allowJs": true,
"strictPropertyInitialization": false,
"forceConsistentCasingInFileNames": true,
"allowSyntheticDefaultImports": true,
"strictNullChecks": true,
"target": "ES2022",
"module": "NodeNext",
"moduleResolution": "NodeNext",
/* Allow decorators */
"experimentalDecorators": true,
"emitDecoratorMetadata": true,
/* Strictness */
"strict": true,
"lib": ["es2022"],
"outDir": "./gen/srv"
},
"include": ["./srv"]
}[!WARNING] If below message appears
----------------------------------------------------------------------- WARNING: Package '@sap/cds' was loaded from different installations: [ '***/node_modules/@sap/cds/lib/index.js', '***/node_modules/@dxfrontier/cds-ts-dispatcher/node_modules/@sap/cds/lib/index.js' ] Rather ensure a single install only to avoid hard-to-resolve errors. -----------------------------------------------------------------------Run the following command :
npm install -g @sap/cds-dk@latest
Generate CDS Typed entities
Execute the following commands :
cds add typernpm install[!TIP] If above option is being used, this means whenever we change a
.CDSfile the changes will reflect in the generated@cds-modelsfolder.
Execute the command :
npx @cap-js/cds-typer "*" --outputDirectory ./srv/util/types/entities- Target folder :
./srv/util/types/entities- Change to your desired destination folder.
Important
[!IMPORTANT] Import always the
generated entitiesfrom theservicefolders and not from theindex.ts
[!TIP] By default cds-typer will create in your
package.jsona quick path alias like :"imports": { "#cds-models/*": "./@cds-models/*/index.js" }Use import helper to import entities from
#cds-modelslike example :
import { Book } from '#cds-models/CatalogService';
Usage
Architecture
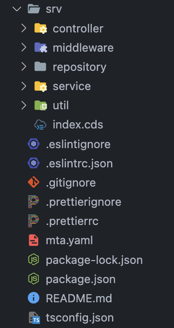
We recommend adhering to the Controller-Service-Repository design pattern using the following folder structure:
- EntityHandler
(Controller)- Responsible for managing the REST interface to the business logic implemented in ServiceLogic - ServiceLogic
(Service)- Contains business logic implementations - Repository
(Repository)- This component is dedicated to handling entity manipulation operations by leveraging the power of CDS-QL.
Controller-Service-Repository suggested folder structure
 <= expanded folders =>
<= expanded folders => 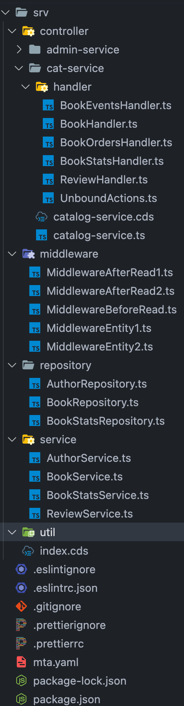
[!TIP] You can have a look over the CDS-TS-Dispatcher-Samples where we use the Controller-Service-Repository pattern and Dispatcher.
CDSDispatcher
CDSDispatcher(entities : Constructable[])
The CDSDispatcher constructor allows you to create an instance for dispatching and managing entities.
Parameters
entities (Array): An array of Entity handler(s) (Constructable) that represent the entities in the CDS.
Method
initialize: Theinitializemethod of theCDSDispatcherclass is used to initialize Entity handler(s) and all of their dependencies : Services, Repositories, UnboundActions
Example
import { CDSDispatcher } from '@dxfrontier/cds-ts-dispatcher';
export = new CDSDispatcher([
// Entities
BookHandler,
ReviewHandler,
BookStatsHandler,
// Draft
BookEventsHandler,
// Unbound actions
UnboundActionsHandler,
]).initialize();
// or use
// module.exports = new CDSDispatcher([ ...Visual image
Decorators
Class
@EntityHandler
The @EntityHandler decorator is utilized at the class-level to annotate a class with:
- A specific
entitythat will serve as the base entity for all handler decorators within the class. '*'asall entitiesthat will serve as the base entity for all handler decorators within the class.
Overloads
| Method | Parameters | Description |
| :----------------------------------- | :--------------------------------------- | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
| 1. EntityHandler(entity: CDSTyper) | Must be a CDS-Typer generated class | It ensures that all handlers within the class operate with the specified entity context. |
| 2. EntityHandler(entity: '*') | A wildcard '*' indicating all entities | It ensures that all handlers within the class operate with a generic context indicating that registered events will be triggered for all all entities (active entities and draft entities) Excluded will be @OnAction(), @OnFunction(), @OnEvent(), @OnError() as these actions belongs to the Service itself. |
Parameters
entity (CDSTyperEntity | '*'): A specialized class generated using the CDS-Typer or generic wild card'*'applicable to all entities.
Example 1 using CDS-Typer
import { EntityHandler } from '@dxfrontier/cds-ts-dispatcher';
import { MyEntity } from 'YOUR_CDS_TYPER_ENTITIES_LOCATION';
@EntityHandler(MyEntity)
export class BookHandler {
// ...
constructor() {}
// All events like @AfterRead, @BeforeRead, ... will be triggered based on 'MyEntity'
}[!TIP] After creation of
BookHandlerclass, you canimport itinto the CDSDispatcher.import { CDSDispatcher } from '@dxfrontier/cds-ts-dispatcher'; export = new CDSDispatcher([ // Entities BookHandler, // Unbound actions // ... ]).initialize();
Example 2 using * wildcard indicating that events will be triggered for all entities
import { EntityHandler, CDS_DISPATCHER } from '@dxfrontier/cds-ts-dispatcher';
@EntityHandler(CDS_DISPATCHER.ALL_ENTITIES) // or use the '*'
export class AllEntities {
// ...
constructor() {}
// All events like @AfterRead, @BeforeRead, ... will be triggered on all entities using wildcard '*'
}[!TIP] After creation of
AllEntitiesclass, you canimport itinto the CDSDispatcher.import { CDSDispatcher } from '@dxfrontier/cds-ts-dispatcher'; export = new CDSDispatcher([ // Entities AllEntities, // Unbound actions // ... ]).initialize();
[!NOTE] MyEntity was generated using CDS-Typer and imported in the class.
@ServiceLogic
@ServiceLogic()
The @ServiceLogic decorator is utilized at the class-level to annotate a class as a specialized class containing only business logic.
Example
import { ServiceLogic } from '@dxfrontier/cds-ts-dispatcher';
@ServiceLogic()
export class CustomerService {
// ...
constructor() {}
// ...
}[!TIP] When applying
@ServiceLogic()decorator, the class becomes eligible to be used with Inject decorator forDependency injection.
@Repository
@Repository()
The @Repository decorator is utilized as a class-level annotation that designates a particular class as a specialized Repository, this class should contain only CDS-QL code.
import { Repository } from '@dxfrontier/cds-ts-dispatcher';
@Repository()
export class CustomerRepository {
// ...
constructor() {}
// ...
}[!TIP] When applying
@Repository()decorator, the class becomes eligible to be used with Inject decorator forDependency injection.
[Optional] - CDS-TS-Repository - BaseRepository
The CDS-TS-Repository - BaseRepository was designed to reduce the boilerplate code required to implement data access layer for persistance entities.
It simplifies the implementation by offering a set of ready-to-use actions for interacting with the database. These actions include:
.create(): Create new records in the database..getAll(): Retrieve all records from the database..find(): Query the database to find specific data..delete(): Remove records from the database..exists(): Check the existence of data in the database.- and many more ...
Example
import { Repository } from '@dxfrontier/cds-ts-dispatcher';
import { BaseRepository } from '@dxfrontier/cds-ts-repository';
import { MyEntity } from 'YOUR_CDS_TYPER_ENTITIES_LOCATION';
@Repository()
export class CustomerRepository extends BaseRepository<MyEntity> {
constructor() {
super(MyEntity);
}
public async aMethod() {
const created = await this.create(...)
const createdMany = await this.createMany(...)
const updated = await this.update(...)
// ...
}
}To get started, refer to the official documentation CDS-TS-Repository - BaseRepository. Explore the capabilities it offers and enhance your data access layer with ease.
[!NOTE] MyEntity was generated using CDS-Typer and imported in the class.
@UnboundActions
@UnboundActions()
The @UnboundActions decorator is utilized at the class-level to annotate a class as a specialized class which will be used only for Unbound actions.
The following decorators can be used inside of @UnboundActions() :
Example
import { UnboundActions, OnAction, OnFunction, OnEvent, Req, Next, Error } from '@dxfrontier/cds-ts-dispatcher';
import { MyAction, MyFunction, MyEvent } from 'YOUR_CDS_TYPER_ENTITIES_LOCATION';
import type { ActionRequest, ActionReturn, Request, NextEvent } from '@dxfrontier/cds-ts-dispatcher';
@UnboundActions()
export class UnboundActionsHandler {
// ... @Inject dependencies, if needed.
constructor() {}
// Unbound action
@OnAction(MyAction)
private async onActionMethod(
@Req() req: ActionRequest<typeof MyAction>,
@Next() next: NextEvent,
): ActionReturn<typeof MyAction> {
// ...
}
// Unbound Function
@OnFunction(MyFunction)
private async onFunctionMethod(
@Req() req: ActionRequest<typeof MyFunction>,
@Next() next: NextEvent,
): ActionReturn<typeof MyFunction> {
// ...
}
// Unbound event
@OnEvent(MyEvent)
private async onEventMethod(@Req() req: Request<MyEvent>) {
// ...
}
// Unbound error
@OnError()
private onErrorMethod(@Error() err: Error, @Req() req: Request) {
// ...
}
}Imported it in the CDSDispatcher
import { CDSDispatcher } from '@dxfrontier/cds-ts-dispatcher';
export = new CDSDispatcher([ UnboundActionsHandler, ...])
// or
// use module.exports = new CDSDispatcher( ... )[!NOTE] The reason behind introducing a distinct decorator for
Unbound actionsstems from the fact that these actions are not associated with any specificEntitybut instead these actions belongs to the Service itself.
@Use
@Use(...Middleware[])
The @Use decorator simplifies the integration of middlewares into your classes.
When @Use decorator applied at the class-level this decorator inject middlewares into the class and gain access to the req: Request and next: NextMiddleware middleware across all events (@AfterRead, @OnRead ...) within that class.
Middleware decorators can perform the following tasks:
- Execute any code.
- Make changes to the request object.
- End the request-response cycle.
- Call the next middleware function in the stack.
- If the current middleware function does not end the request-response cycle, it must call
next()to pass control to the next middleware function. Otherwise, the request will be left hanging.
Parameters
...Middleware[]): Middleware classes to be injected.
Example: middleware implementation
import type { MiddlewareImpl, NextMiddleware, Request } from '@dxfrontier/cds-ts-dispatcher';
export class MiddlewareClass implements MiddlewareImpl {
public async use(req: Request, next: NextMiddleware) {
console.log('Middleware use method called.');
await next(); // call next middleware
}
}Example usage
import { EntityHandler, Use, Inject, CDS_DISPATCHER } from '@dxfrontier/cds-ts-dispatcher';
import { MyEntity } from 'YOUR_CDS_TYPER_ENTITIES_LOCATION';
import { Middleware1, Middleware2, MiddlewareN } from 'YOUR_MIDDLEWARE_LOCATION';
import type { Service } from '@dxfrontier/cds-ts-dispatcher';
@EntityHandler(MyEntity)
@Use(Middleware1, Middleware2, MiddlewareN)
export class CustomerHandler {
// ...
@Inject(CDS_DISPATCHER.SRV) private srv: Service;
// ...
constructor() {}
// ...
}[!TIP]
- Think of it (middleware) like as a reusable class, enhancing the functionality of all events within the class.
- Middlewares when applied with
@Useare executed before the normal events.- If you need to apply middleware to a
methodyou should use the method specific @Use decorator .
[!WARNING] If
req.reject()is used inside of middleware this will stop the stack of middlewares, this means that next middleware will not be executed.
[!NOTE] MyEntity was generated using CDS-Typer and imported in the class.
Field
@Inject
@Inject(serviceIdentifier: ServiceIdentifierOrFunc<unknown>)
The @Inject decorator is utilized as a field-level decorator and allows you to inject dependencies into your classes.
Parameters
serviceIdentifier(ServiceIdentifierOrFunc<unknown>): A Class representing the service to inject.
Example
import { EntityHandler, Inject, CDS_DISPATCHER } from "@dxfrontier/cds-ts-dispatcher";
import type { Service } from '@dxfrontier/cds-ts-dispatcher';
import { MyEntity } from 'YOUR_CDS_TYPER_ENTITIES_LOCATION';
@EntityHandler(MyEntity)
export class CustomerHandler {
...
@Inject(CustomerService) private customerService: CustomerService
@Inject(CustomerRepository) private customerService: CustomerRepository
@Inject(AnyOtherInjectableClass) private repository: AnyOtherInjectableClass
@Inject(CDS_DISPATCHER.SRV) private srv: Service
// ...
constructor() {}
// ...
}[!NOTE] MyEntity was generated using CDS-Typer and imported in the class.
@Inject(CDS_DISPATCHER.SRV)
@Inject(CDS_DISPATCHER.SRV) private srv: Service
This specialized @Inject can be used as a constant in and contains the CDS.ApplicationService for further enhancements.
It can be injected in the following :
Example
import { EntityHandler, Inject, CDS_DISPATCHER } from '@dxfrontier/cds-ts-dispatcher';
import { MyEntity } from 'YOUR_CDS_TYPER_ENTITIES_LOCATION';
import type { Service } from '@dxfrontier/cds-ts-dispatcher';
@EntityHandler(MyEntity)
// OR @ServiceLogic()
// OR @Repository()
// OR @UnboundActions()
export class CustomerHandler {
// @Inject dependencies
@Inject(CDS_DISPATCHER.SRV) private readonly srv: Service;
constructor() {}
// ...
}[!TIP] The CDS.ApplicationService can be accessed trough
this.srv.
[!NOTE] MyEntity was generated using CDS-Typer and imported in the the class.
@Inject(CDS_DISPATCHER.OUTBOXED_SRV)
@Inject(CDS_DISPATCHER.OUTBOXED_SRV) private srv: Service
This specialized @Inject can be used as a constant and contains the CDS.outboxed service.
It can be injected in the following :
Example
import { EntityHandler, Inject, CDS_DISPATCHER } from '@dxfrontier/cds-ts-dispatcher';
import { MyEntity } from 'YOUR_CDS_TYPER_ENTITIES_LOCATION';
import type { Service } from '@dxfrontier/cds-ts-dispatcher';
@EntityHandler(MyEntity)
// OR @ServiceLogic()
// OR @Repository()
// OR @UnboundActions()
export class CustomerHandler {
// @Inject dependencies
@Inject(CDS_DISPATCHER.OUTBOXED_SRV) private readonly outboxedSrv: Service;
constructor() {}
// ...
}[!TIP] More info about
outboxedca be found at SAP CAP Node.js Outboxed
[!TIP] The CDS.ApplicationService can be accessed trough
this.outboxedSrv
[!NOTE] MyEntity was generated using CDS-Typer and imported in the the class.
Parameter
@Req
@Req()
The @Req decorator is utilized at the parameter level to annotate a parameter with the Request object, providing access to request-related information of the current event.
Return
Request: An instance of@sap/cds-Request
Example
import { EntityHandler, Req, Results } from '@dxfrontier/cds-ts-dispatcher';
import { MyEntity } from 'YOUR_CDS_TYPER_ENTITIES_LOCATION';
import type { Request } from '@dxfrontier/cds-ts-dispatcher';
@EntityHandler(MyEntity)
export class BookHandler {
// ...
constructor() {}
// ... all events like @AfterRead, @BeforeRead ...
@AfterRead()
private async aMethod(@Req() req: Request, @Results() results: MyEntity[]) {
// ... req...
}
}@Res
@Res()
The @Res decorator is utilized at the parameter level to annotate a parameter with the Request.http.res - (Response) object, providing access to response-related information of the current event and it can be used to enhance the Response.
Return
RequestResponse: An instance ofRequestResponseproviding you response-related information.
Example
import { EntityHandler, Req, Results } from '@dxfrontier/cds-ts-dispatcher';
import { MyEntity } from 'YOUR_CDS_TYPER_ENTITIES_LOCATION';
import type { Request, RequestResponse } from '@dxfrontier/cds-ts-dispatcher';
@EntityHandler(MyEntity)
export class BookHandler {
// ...
constructor() {}
// ... all events like @AfterRead, @BeforeRead ...
@AfterRead()
private async aMethod(@Req() req: Request, @Res() response: RequestResponse, @Results() results: MyEntity[]) {
// Example: we assume we want to add a new header language on the response
// We use => res.setHeader('Accept-Language', 'DE_de');
}
}[!TIP] Decorator
@Rescan be used in all After, Before and On events.
@Results / @Result
@Results() / @Result
The @Results decorator is utilized at the parameter level to annotate a parameter with the request Results.
Return
Array / object: Contains the OData RequestBody.
Example
import { EntityHandler, Req, Results } from '@dxfrontier/cds-ts-dispatcher';
import { MyEntity } from 'YOUR_CDS_TYPER_ENTITIES_LOCATION';
import type { Request } from '@dxfrontier/cds-ts-dispatcher';
@EntityHandler(MyEntity)
export class BookHandler {
// ...
constructor() {}
// ... all events like @AfterRead, @BeforeRead ...
@AfterRead()
private async aMethod(@Req() req: Request, @Results() results: MyEntity[]) {
// ...
}
}[!TIP] When using @AfterCreate(), @AfterUpdate() and @AfterDelete() it's recommended to use the
@Resultdecorator for single object result and@Resultsfor arrays of objects.
@AfterCreate()
@AfterUpdate()
private async aMethod(
@Result() result: Book, // <== @Result() decorator used to annotate it's a an object and not an array
@Req() req: Request,
) {
// ...
}
@AfterRead()
private async aMethod(
@Results() result: Book[], // <== @Results() decorator used to annotate as array of objects
@Req() req: Request,
) {
// ...
}
@AfterDelete()
private async aMethod(
@Result() deleted: boolean, // <== @Result() decorator used to annotate as a boolean
@Req() req: Request,
) {
// ...
}[!TIP] Decorators
@Results()and@Result()can be applied to all After events.
@Next
@Next()
The @Next decorator is utilized at the parameter level to annotate a parameter with the Next function, which is used to proceed to the next event in the chain of execution.
Return
NextEvent: The next event in chain to be called.
Example
import { EntityHandler, Req, Results } from '@dxfrontier/cds-ts-dispatcher';
import { MyEntity } from 'YOUR_CDS_TYPER_ENTITIES_LOCATION';
import type { Request, NextEvent } from '@dxfrontier/cds-ts-dispatcher';
@EntityHandler(MyEntity)
export class BookHandler {
// ...
constructor() {}
// ... all events like @AfterRead, @BeforeRead, @OnCreate ...
@OnCreate()
public async onCreate(@Req() req: Request<MyEntity>, @Next() next: NextEvent) {
return next();
}
}[!TIP] Decorator
@Nextcan be applied to all On, On - draft event decorators.
@Error
@Error()
The @Error decorator is utilized at the parameter level to annotate a parameter with the Error and contains information regarding the failed Request.
Return
Error: An instance of typeError.
Example
import { UnboundActions, Req, Error } from '@dxfrontier/cds-ts-dispatcher';
import { MyEntity } from 'YOUR_CDS_TYPER_ENTITIES_LOCATION';
import type { Request } from '@dxfrontier/cds-ts-dispatcher';
@UnboundActions()
export class UnboundActionsHandler {
// ...
constructor() {}
@OnError()
public onError(@Error() err: Error, @Req() req: Request): void {
// ...
}
}[!TIP] Decorator
@Errorcan be applied to @OnError() decorator which resides inside of the @UnboundActions().
@Jwt
@Jwt()
The @Jwt decorator is utilized at the parameter level. It will retrieve the to retrieve JWT from the Request that is based on the node req.http.req - IncomingMessage.
Fails if no authorization header is given or has the wrong format.
Return
string|undefined: The retrievedJWT tokenor undefined if no token was found.
Example
import { EntityHandler, Req, Results, Jwt } from '@dxfrontier/cds-ts-dispatcher';
import { MyEntity } from 'YOUR_CDS_TYPER_ENTITIES_LOCATION';
import type { Request } from '@dxfrontier/cds-ts-dispatcher';
@EntityHandler(MyEntity)
export class BookHandler {
// ...
constructor() {}
// ... all events like @AfterRead, @BeforeRead ...
@AfterRead()
private async aMethod(@Req() req: Request, @Results() results: MyEntity[], @Jwt() jwt: string | undefined) {
// ... req...
}
}[!IMPORTANT] Expected format is
Bearer <TOKEN>.
@IsPresent
@IsPresent<Key extends CRUDQueryKeys>(key: Key, property: PickQueryPropsByKey<Key>)
The @IsPresent decorator is utilized at the parameter level. It allows you to verify the existence of a specified Query property values.
Parameters
key (string): Specifies the type of query operation. Accepted values areINSERT,SELECT,UPDATE,UPSERT,DELETE.property (string): Specifies the property based on thekey.
Return
boolean: This decorator returnstrueifpropertyvalueis filled,falseotherwise
Example
import { EntityHandler, Req, Results, IsPresent } from '@dxfrontier/cds-ts-dispatcher';
import { MyEntity } from 'YOUR_CDS_TYPER_ENTITIES_LOCATION';
import type { Request } from '@dxfrontier/cds-ts-dispatcher';
@EntityHandler(MyEntity)
class BookHandler {
// ...
constructor() {}
@AfterRead()
private async aMethod(
@Req() req: Request,
@Results() results: MyEntity[],
@IsPresent('SELECT', 'columns') columnsPresent: boolean,
) {
if (columnsPresent) {
// ...
}
// ...
}
}[!TIP] Decorator @IsPresent() works well with @GetQuery().
@IsRole
@IsRole(...roles: string[])
The @IsRole decorator is utilized at the parameter level. It allows you to verify
if the User has assigned a given role.
It applies an logical OR on the specified roles, meaning it checks if at least one of the specified roles is assigned
Parameters
role (...string[]): An array of role names to check if are assigned.
Return
boolean: This decorator returnstrueif at least one of the specified roles is assigned to the current request user, otherwisefalse.
Example
import { EntityHandler, Req, Results, IsPresent, IsRole } from '@dxfrontier/cds-ts-dispatcher';
import { MyEntity } from 'YOUR_CDS_TYPER_ENTITIES_LOCATION';
import type { Request } from '@dxfrontier/cds-ts-dispatcher';
@EntityHandler(MyEntity)
class BookHandler {
// ...
constructor() {}
@AfterRead()
private async aMethod(
@Req() req: Request,
@Results() results: MyEntity[],
@IsRole('role', 'anotherRole') roleAssigned: boolean,
) {
if (roleAssigned) {
// ...
}
// ...
}
}[!TIP] The role names correspond to the values of
@requiresand the@restrict.grants.toannotations in yourCDSmodels.
@IsColumnSupplied
@IsColumnSupplied<T>(field : keyof T)
The @IsColumnSupplied<T>(field : keyof T) decorator is utilized at the parameter level. It allows your to verify the existence of a column in the SELECT, INSERT or UPSERT Query.
Parameters
field (string): A string representing the name of the column to be verified.
Type Parameters
T: The entity type (e.g.,MyEntity) representing the table or collection on which the decorator operates. This allows TypeScript to enforce type safety for the field parameter.
Return :
boolean: This decorator returnstrueiffield / columnwas found,falseotherwise
Example
import { EntityHandler, Req, Results, IsPresent } from '@dxfrontier/cds-ts-dispatcher';
import { MyEntity } from 'YOUR_CDS_TYPER_ENTITIES_LOCATION';
import type { Request } from '@dxfrontier/cds-ts-dispatcher';
@EntityHandler(MyEntity)
class BookHandler {
// ...
constructor() {}
@AfterRead()
private async aMethod(
@Req() req: Request,
@Results() results: MyEntity[],
@IsColumnSupplied<MyEntity>('price') priceSupplied: boolean,
) {
if (priceSupplied) {
// ...
}
// ...
}
}@GetQuery
@GetQuery<Key extends CRUDQueryKeys>(key: Key, property: PickQueryPropsByKey<Key>)
The @GetQuery decorator is utilized at the parameter level. It allows you to retrieve Query property values.
Parameters
key (string): Specifies the type of query operation. Accepted values areINSERT,SELECT,UPDATE,UPSERT,DELETE.property (string): Specifies the property based on thekey.
Return: Varies based on the specified property :
- @GetQuery(
'SELECT','columns') columns:GetQueryType['columns']['forSelect'] - @GetQuery(
'SELECT','distinct') distinct:GetQueryType['distinct'] - @GetQuery(
'SELECT','excluding') excluding:GetQueryType['excluding'] - @GetQuery(
'SELECT','from') from:GetQueryType['from']['forSelect'] - @GetQuery(
'SELECT','groupBy') groupBy:GetQueryType['groupBy'] - @GetQuery(
'SELECT','having') having:GetQueryType['having'] - @GetQuery(
'SELECT','limit') limit:GetQueryType['limit'] - @GetQuery(
'SELECT','limit.rows') limitRows:GetQueryType['limit']['rows'] - @GetQuery(
'SELECT','limit.offset') limitOffset:GetQueryType['limit']['offset'] - @GetQuery(
'SELECT','mixin') mixin:GetQueryType['mixin'] - @GetQuery(
'SELECT','one') one:GetQueryType['one'] - @GetQuery(
'SELECT','orderBy') orderBy:GetQueryType['orderBy'] - @GetQuery(
'SELECT','where') where:GetQueryType['where']
- @GetQuery(
- @GetQuery(
'INSERT','as') as:GetQueryType['as'] - @GetQuery(
'INSERT','columns') columns:GetQueryType['columns']['forInsert'] - @GetQuery(
'INSERT','entries') entries:GetQueryType['entries'] - @GetQuery(
'INSERT','into') into:GetQueryType['into'] - @GetQuery(
'INSERT','rows') rows:GetQueryType['rows'] - @GetQuery(
'INSERT','values') values:GetQueryType['values']
- @GetQuery(
- @GetQuery(
'UPDATE','data') data:GetQueryType['data'] - @GetQuery(
'UPDATE','entity') entity:GetQueryType['entity'] - @GetQuery(
'UPDATE','where') where:GetQueryType['where']
- @GetQuery(
- @GetQuery(
'UPSERT','columns') columns:GetQueryType['columns'][forUpsert] - @GetQuery(
'UPSERT','entries') entries:GetQueryType['entries'] - @GetQuery(
'UPSERT','into') into:GetQueryType['into'] - @GetQuery(
'UPSERT','rows') rows:GetQueryType['rows'] - @GetQuery(
'UPSERT','values') values:GetQueryType['values']
- @GetQuery(
@GetQuery(
'DELETE','from') from:GetQueryType['from'][forDelete]@GetQuery(
'DELETE','where') columns:GetQueryType['where']
Example
import { EntityHandler, Req, Results, IsPresent, GetQuery } from '@dxfrontier/cds-ts-dispatcher';
import { MyEntity } from 'YOUR_CDS_TYPER_ENTITIES_LOCATION';
import type { Request, GetQueryType } from '@dxfrontier/cds-ts-dispatcher';
@EntityHandler(MyEntity)
class BookHandler {
// ...
constructor() {}
@AfterRead()
private async aMethod(
@Req() req: Request,
@Results() results: MyEntity[],
// Check existence of columns
@IsPresent('SELECT', 'columns') columnsPresent: boolean,
// Get columns
@GetQuery('SELECT', 'columns') columns: GetQueryType['columns']['forSelect'],
@GetQuery('SELECT', 'orderBy') orderBy: GetQueryType['orderBy'],
@GetQuery('SELECT', 'groupBy') groupBy: GetQueryType['groupBy'],
) {
if (columnsPresent) {
// do something with columns values
// columns.forEach(...)
}
// ...
}
}[!TIP] Decorator @GetQuery() can be used to get the Query property and @IsPresent() can check if the Query property is empty or not.
@GetRequest
@GetRequest(property : keyof Request)
The @GetRequest decorator is utilized at the parameter level. It allows you to retrieve the specified property value from the Request object.
Parameters
property (string): Specifies the property to retrieve from theRequestobject.
Return: Varies based on the specified property :
- @GetRequest(
'entity') entity:Request['entity'], - @GetRequest(
'event') event:Request['event'], - @GetRequest(
'features') features:Request['features'], - @GetRequest(
'headers') headers:Request['headers'], - @GetRequest(
'http') http:Request['http'], - @GetRequest(
'id') id:Request['id'], - @GetRequest(
'locale') locale:Request['locale'], - @GetRequest(
'method') method:Request['method'], - @GetRequest(
'params') params:Request['params'], - @GetRequest(
'query') query:Request['query'], - @GetRequest(
'subject') subject:Request['subject'], - @GetRequest(
'target') target:Request['target'], - @GetRequest(
'tenant') tenant:Request['tenant'], - @GetRequest(
'timestamp') timestamp:Request['timestamp'], - @GetRequest(
'user') user:Request['user'],
Example
import { EntityHandler, Results, GetRequest } from '@dxfrontier/cds-ts-dispatcher';
import { MyEntity } from 'YOUR_CDS_TYPER_ENTITIES_LOCATION';
import type { Request } from '@dxfrontier/cds-ts-dispatcher';
@EntityHandler(MyEntity)
class BookHandler {
// ...
constructor() {}
@AfterRead()
private async aMethod(
// @Req() req: Request, we assume we don't need the hole Request object and we need only 'locale' and 'method'
@Results() results: MyEntity[],
@GetRequest('locale') locale: Request['locale'],
@GetRequest('method') method: Request['method'],
) {
// do something with 'locale' and 'method' ...
}
}[!TIP] Type
Requestcan be import from :import type { Request } from '@dxfrontier/cds-ts-dispatcher';
@SingleInstanceSwitch
@SingleInstanceSwitch
The @SingleInstanceSwitch() decorator is applied at the parameter level.
It allows you to manage different behaviors based on whether the request is for a single entity instance or an entity set, the parameter assigned to the decorator will behave like a switch.
Return
truewhen theRequestissingle instancefalsewhen theRequestisentity set
Example 1
Single request : http://localhost:4004/odata/v4/main/`MyEntity(ID=2f12d711-b09e-4b57-b035-2cbd0a023a09)`
import { AfterRead, SingleInstanceCapable } from "@dxfrontier/cds-ts-dispatcher";
import type { Request } from '@dxfrontier/cds-ts-dispatcher';
import { MyEntity } from 'YOUR_CDS_TYPER_ENTITIES_LOCATION';
@AfterRead()
private async singeInstanceMethodAndEntitySet(@Results() results : MyEntity[], @Req() req: Request<MyEntity>, @SingleInstanceSwitch() isSingleInstance: boolean) {
if(isSingleInstance) {
// This will be executed only when single instance is called : http://localhost:4004/odata/v4/main/MyEntity(ID=2f12d711-b09e-4b57-b035-2cbd0a023a09)
return this.customerService.handleSingleInstance(req)
}
// nothing to entity set
}Example 2
Entity request : http://localhost:4004/odata/v4/main/`MyEntity`
import { AfterRead, SingleInstanceCapable } from "@dxfrontier/cds-ts-dispatcher";
import type { Request } from '@dxfrontier/cds-ts-dispatcher';
import { MyEntity } from 'YOUR_CDS_TYPER_ENTITIES_LOCATION';
@AfterRead()
private async singeInstanceMethodAndEntitySet(@Results() results : MyEntity[], @Req() req: Request<MyEntity>, @SingleInstanceSwitch() isSingleInstance: boolean) {
if(isSingleInstance) {
// This will be executed only when single instance is called : http://localhost:4004/odata/v4/main/MyEntity(ID=2f12d711-b09e-4b57-b035-2cbd0a023a09)
// ...
}
// ... this will be executed when entity set is called : http://localhost:4004/odata/v4/main/MyEntity
results[0] = {
name : 'new value'
}
}[!TIP] Decorator
@SingleInstanceSwitchcan be used together with the following decorator events:
[!NOTE] MyEntity was generated using CDS-Typer and imported in the the class.
@ValidationResults
@ValidationResults
The @ValidationResults decorator allows to capture and inject validation results directly into a method parameter, allowing access to individual validation flags within the decorated method.
When used alongside the @Validate decorator, it enables you to perform conditional logic based on specific validation outcomes.
Example
@BeforeCreate()
@Validate<MyEntity>({ action: 'isLowercase', exposeValidatorResult: true }, 'comment')
@Validate<MyEntity>({ action: 'endsWith', target: 'N', exposeValidatorResult: true }, 'description')
public async beforeCreate(
@Req() req: Request<MyEntity>,
@ValidationResults() validator: ValidatorFlags<'isLowercase' | 'endsWith'>
) {
// Conditional handling based on validation flags
if (validator.isLowercase) {
// Execute logic when field `comment` is lowercase
}
else {
// Execute logic when field `comment` is not lowercase
}
if (validator.endsWith) {
// Execute logic when field `description` is endsWith with letter 'N'
}
else {
// Execute logic when field `description` doesn't endsWith with letter 'N'
}
}[!IMPORTANT] For
@ValidationResultsto work, each @Validate decorator must set theexposeValidatorResultoption totrue. This ensures that the validation results are available as flags in the method.
@Locale
@Locale
Parameter decorator used to inject locale information into a method parameter.
Example
@BeforeCreate()
public async beforeCreate(
@Req() req: Request<MyEntity>,
@Locale() locale: string
) {
if (locale === 'en-US') {
// handle logic specific to the 'en-US' locale
}
}@Env
@Env<T>(env: PropertyStringPath<T>)
The @Env decorator is a parameter decorator used to inject values from the cds.env configuration object directly into a method parameter.
Parameters
env (string): A string path representing a property fromcds.env. This path follows the formatproperty string path, which allows access to deeply nested configuration properties.- E.g. :
'requires.db.credentials.url'corresponds to cds.env.requires.db.credentials.url object.
- E.g. :
Type Parameters
T: TheCDS environmental variablestype (e.g.,cds env get) representing the collection on which the decorator operates. This allows TypeScript to enforce type safety.
Return :
- The decorator returns the value of the specified
cds.envproperty value.
Example
import { CDS_ENV } from '#dispatcher';
@BeforeCreate()
public async beforeCreate(
@Req() req: Request<MyEntity>,
@Env<CDS_ENV>('requires.db.credentials.url') dbUrl: CDS_ENV['requires']['db']['credentials']['url'],
// or @Env<CDS_ENV>('requires.db.credentials.url') dbUrl: string
// or @Env<CDS_ENV>('requires.db.credentials.url') dbUrl: any
// or any other type if you do not want to use the CDS_ENV generated types
) {
if (dbUrl) {
// handle custom logic ...
}
}[!NOTE] When you install cds-ts-dispatcher
(e.g. npm install @dxfrontier/cds-ts-dispatcher)or run a generalnpm install, the following will be generated or updated :
- New
@dispatcherfolder is generated at the project root. This folder contains theCDS ENV TS interfaces, generated based on the structure of your currentcds.envproject specific configuration (retrieved fromcds env getcli command).... @dispatcher ...
package.jsonwill be updated with a newimport:"imports": { "#dispatcher": "./@dispatcher/index.js" }
tsconfig.jsonwill be updated:"include": [ "...", "./@dispatcher" ]
.gitignorewill be updated::... @dispatcher
[!NOTE] The
@dispatcherfolder is regenerated each time you run npm install.
[!TIP] You can import the generated
CDS envfrom the generated@dispatcherfolder by using :import { CDS_ENV } from '#dispatcher';
Method-active entity
Before
Use @BeforeCreate(), @BeforeRead(), @BeforeUpdate(), @BeforeDelete() to register handlers to run before .on handlers, frequently used for validating user input.
The handlers receive one argument:
reqof typeRequest
See also the official SAP JS CDS-Before event
[!TIP] If
@odata.draft.enabled: trueto manage event handlers for draft version you can use
@BeforeCreateDraft()@BeforeReadDraft()@BeforeUpdateDraft()@BeforeDeleteDraft()
@BeforeCreate
@BeforeCreate()
Example
import { BeforeCreate } from "@dxfrontier/cds-ts-dispatcher";
import type { Request } from '@dxfrontier/cds-ts-dispatcher';
import { MyEntity } from 'YOUR_CDS_TYPER_ENTITIES_LOCATION';
@BeforeCreate()
private async beforeCreateMethod(@Req() req: Request<MyEntity>) {
// ...
}Equivalent to 'JS'
this.before('CREATE', MyEntity, async (req) => {
// ...
});[!IMPORTANT] It is important to note that the decorator
@BeforeCreate()will be triggered based on the EntityHandlerargument=>MyEntity.
[!NOTE] MyEntity was generated using CDS-Typer and imported in the the class.
@BeforeRead
@BeforeRead()
Example
import { BeforeRead } from "@dxfrontier/cds-ts-dispatcher";
import type { Request } from '@dxfrontier/cds-ts-dispatcher';
import { MyEntity } from 'YOUR_CDS_TYPER_ENTITIES_LOCATION';
@BeforeRead()
private async beforeReadMethod(@Req() req: Request<MyEntity>) {
// ...
}Equivalent to 'JS'
this.before('READ', MyEntity, async (req) => {
// ...
});[!IMPORTANT] Decorator
@BeforeRead()will be triggered based on the EntityHandlerargument=>MyEntity.
[!NOTE] MyEntity was generated using CDS-Typer and imported in the the class.
@BeforeUpdate
@BeforeUpdate()
Example
import { BeforeUpdate } from "@dxfrontier/cds-ts-dispatcher";
import type { Request } from '@dxfrontier/cds-ts-dispatcher';
import { MyEntity } from 'YOUR_CDS_TYPER_ENTITIES_LOCATION';
@BeforeUpdate()
private async beforeUpdateMethod(@Req() req: Request<MyEntity>) {
// ...
}Equivalent to 'JS'
this.before('UPDATE', MyEntity, async (req) => {
// ...
});[!IMPORTANT] Decorator
@BeforeUpdate()will be triggered based on the EntityHandlerargument=>MyEntity
[!NOTE] MyEntity was generated using CDS-Typer and imported in the the class.
@BeforeDelete
@BeforeDelete()
Example
import { BeforeDelete } from "@dxfrontier/cds-ts-dispatcher";
import type { Request } from '@dxfrontier/cds-ts-dispatcher';
import { MyEntity } from 'YOUR_CDS_TYPER_ENTITIES_LOCATION';
@BeforeDelete()
private async beforeDeleteMethod(@Req() req: Request<MyEntity>) {
// ...
}Equivalent to 'JS'
this.before('DELETE', MyEntity, async (req) => {
// ...
});[!IMPORTANT] Decorator
@BeforeDelete()will be triggered based on the EntityHandlerargument=>MyEntity.
[!NOTE] MyEntity was generated using CDS-Typer and imported in the the class.
@BeforeAll
The @BeforeAll decorator is triggered whenever any CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete) event occurs, whether the entity is active or in draft mode.
ACTIVE ENTITY
For active entities, the @BeforeAll decorator will be triggered when at least one of the following events occurs:
CREATE@BeforeCreate(), @AfterCreate(), @OnCreate()READ@BeforeRead(), @AfterRead(), @OnRead()UPDATE@BeforeUpdate(), @AfterUpdate(), @OnUpdate()DELETE@BeforeDelete(), @AfterDelete(), @OnDelete()BOUND ACTIONS@OnBoundAction()BOUND FUNCTIONS@OnBoundFunction()
DRAFT
For draft entities, the @BeforeAll decorator will be triggered when at least one of the following events occurs:
CREATE@BeforeNewDraft(), @AfterNewDraft(), @OnNewDraft()CANCEL@BeforeCancelDraft(), @AfterCancelDraft(), @OnCancelDraft()EDIT@BeforeEditDraft(), @AfterEditDraft(), @OnEditDraft()SAVE@BeforeSaveDraft(), @AfterSaveDraft(), @OnSaveDraft()- :heavy_plus_sign: All active entity Before, After, On events which have a
Draftvariant.
@BeforeAll()
Example
import { BeforeAll } from "@dxfrontier/cds-ts-dispatcher";
import type { Request } from '@dxfrontier/cds-ts-dispatcher';
import { MyEntity } from 'YOUR_CDS_TYPER_ENTITIES_LOCATION';
@BeforeAll()
private async beforeAllEvents(@Req() req: Request<MyEntity>) {
// ...
}Equivalent to 'JS'
this.before('*', MyEntity, async (req) => {
// ...
});[!IMPORTANT] Decorator
@BeforeAll()will be triggered based on the EntityHandlerargument=>MyEntity.
[!TIP] If the entity has drafts enabled
@odata.draft.enabled: true, the@BeforeAlldecorator will still be triggered for draft events.
[!NOTE] MyEntity was generated using CDS-Typer and imported in the the class.
After
Use @AfterCreate(), @AfterRead(), @AfterUpdate(), @AfterDelete() register handlers to run after the .on handlers, frequently used to enrich outbound data.
The handlers receive two arguments:
| Parameters | Decorator | Description |
| -------------- | --------------------------------- | -------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
| results, req | @AfterRead | An array of type MyEntity[] and the Request. |
| result, req | @AfterUpdate @AfterCreate | An object of type MyEntity and the Request. |
| deleted, req | @AfterDelete | A boolean indicating whether the instance was deleted and the Request. |
[!TIP] If
@odata.draft.enabled: trueto manage event handlers for draft version you can use :
@AfterCreateDraft()@AfterReadDraft()@AfterReadDraftSingleInstance()@AfterUpdateDraft()@AfterDeleteDraft()
@AfterCreate
@AfterCreate()
Example
import { AfterCreate } from "@dxfrontier/cds-ts-dispatcher";
import type { Request } from '@dxfrontier/cds-ts-dispatcher';
import { MyEntity } from 'YOUR_CDS_TYPER_ENTITIES_LOCATION';
@AfterCreate()
private async afterCreateMethod(@Result() result: MyEntity, @Req() req: Request<MyEntity>) {
// ...
}Equivalent to 'JS'
this.after('CREATE', MyEntity, async (result, req) => {
// ...
});[!IMPORTANT] Decorator
@AfterCreate()will be triggered based on the EntityHandlerargument=>MyEntity.
[!NOTE] MyEntity was generated using CDS-Typer and imported in the the class.
@AfterRead
@AfterRead()
Example
import { AfterRead, Results, Req } from "@dxfrontier/cds-ts-dispatcher";
import type { Request } from '@dxfrontier/cds-ts-dispatcher';
import { MyEntity } from 'YOUR_CDS_TYPER_ENTITIES_LOCATION';
@AfterRead()
private async afterReadMethod(@Results() results: MyEntity[], @Req() req: Request<MyEntity>) {
// ...
}Equivalent to 'JS'
this.after('READ', MyEntity, async (results, req) => {
// ...
});[!IMPORTANT] Decorator
@AfterRead()will be triggered based on the EntityHandlerargumentMyEntity.
[!NOTE] MyEntity was generated using CDS-Typer and imported in the the class.
@AfterReadEachInstance
@AfterReadEachInstance()
The @AfterReadEachInstance decorator is used to execute custom logic after performing a read operation on each individual instance. This behavior is analogous to the JavaScript Array.prototype.forEach method.
Example
import { AfterReadEachInstance, Result, Req } from "@dxfrontier/cds-ts-dispatcher";
import type { Request } from '@dxfrontier/cds-ts-dispatcher';
import { MyEntity } from 'YOUR_CDS_TYPER_ENTITIES_LOCATION';
@AfterReadEachInstance()
private async afterEach(@Result() result: MyEntity, @Req() req: Request<MyEntity>) {
// ...
}Equivalent to 'JS'
this.after('each', MyEntity, async (result, req) => {
// ...
});[!IMPORTANT] Decorator
@AfterReadEachInstance()will be triggered based on the EntityHandlerargumentMyEntity.
[!NOTE] MyEntity was generated using CDS-Typer and imported in the the class.
@AfterUpdate
@AfterUpdate()
Example
Single request : http://localhost:4004/odata/v4/main/`MyEntity(ID=2f12d711-b09e-4b57-b035-2cbd0a023a09)`
import { AfterUpdate } from "@dxfrontier/cds-ts-dispatcher";
import type { Request } from '@dxfrontier/cds-ts-dispatcher';
import { MyEntity } from 'YOUR_CDS_TYPER_ENTITIES_LOCATION';
@AfterUpdate()
private async afterUpdateMethod(@Result() result: MyEntity, @R


