@cafebazaar/async-actions
v0.4.4
Published
<p align="center"> <img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/2771377/95751339-57fbe900-0cab-11eb-8eda-39d8e2807fca.png" /> </p>
Downloads
28
Readme
Overview
Handling async actions(like API calls) is so tedious. Showing loading state and handling options like debouncing needs a lot of code duplications.
Async-Actions proposes a more efficient way of handling those actions without code duplications.
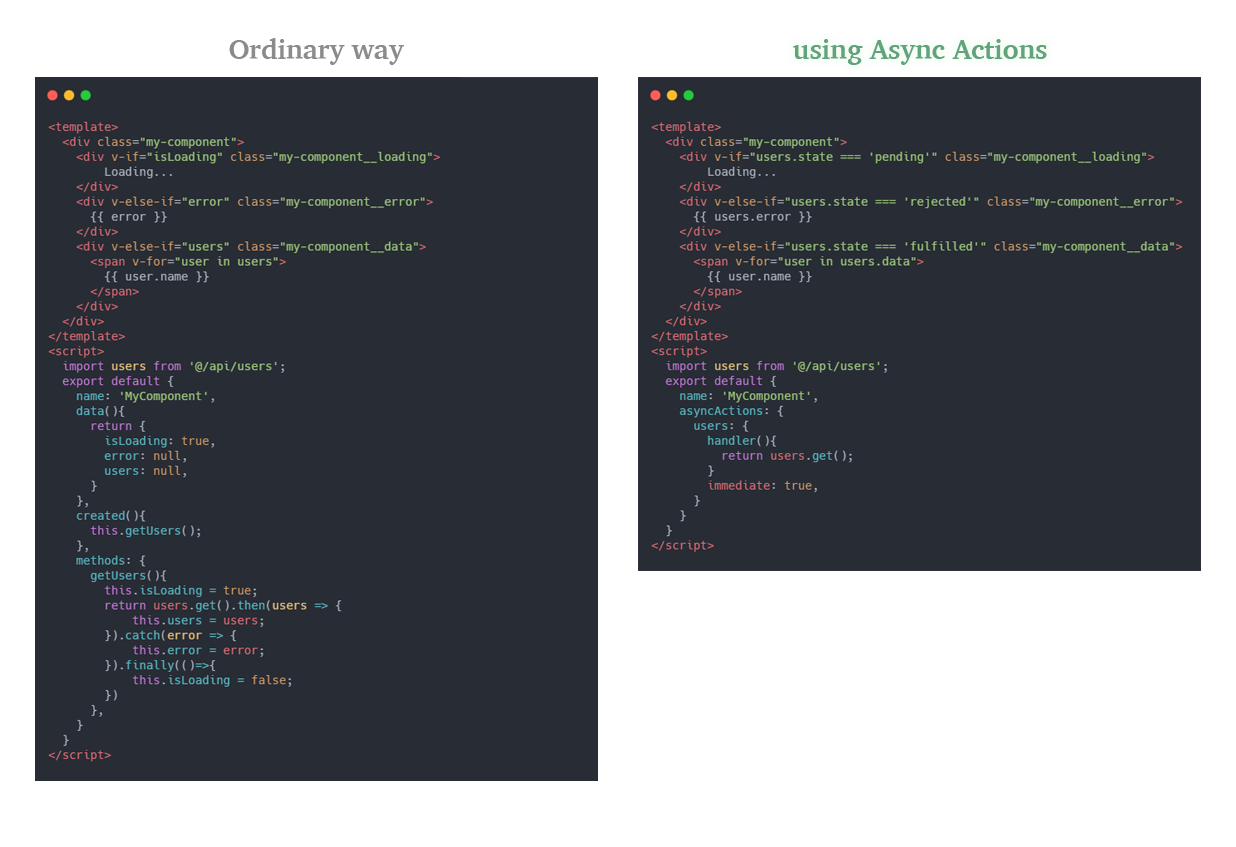
How It Works
Actions are just simple functions. Async-Actions adds state, error, and data properties to your functions and dynamically updates these properties.
Action lifecycle and possible values of the state property
| Value | Description |
| ------------ | ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
| notInitiated | Action has not been called yet. |
| pending | Action has been called, but it has not been completed yet. |
| fulfilled | Action has been completed successfully, and the result value is accessible using the data property. |
| rejected | Action has been rejected with an error which is accessible using error property. |
Installation
You can install Async-Actions with NPM or Yarn.
npm install @cafebazaar/async-actions --saveor
yarn add @cafebazaar/async-actionsUsage
You can use Async-Actions in pure JS. Also there are built in extensions for Vue.js and Svelte.
Vue.js
Vue.observable provided by default as the observable function in the Vue version, and you don't need to pass it. There are two ways to use Async-Actions in a Vue.js project.
1. Define actions in component options
For declaring async-actions in this way, you need to import the plugin and use it as a Vue plugin to enable the functionality globally on all components.
import Vue from 'vue';
import AsyncActions from '@cafebazaar/async-actions/vue';
Vue.use(AsyncActions);Then, you can define async-actions in all components using asyncActions property.
<template>
<div>
<div v-if="getUsers.state === 'pending'">
Fetching Users List. Please Wait...
</div>
<div v-else-if="getUsers.error">
Oops. Somthing Went Wrong :(
</div>
<div v-else>
<ul>
<li v-for="user in getUsers.data" :key="user.id">
{{ user.name }}
</li>
</ul>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'UsersList',
asyncActions: {
getUsers: {
handler() {
return someApiCall();
},
immediate: true,
initialData: [],
// other options...
},
},
};
</script>The List of all options is available here.
If an action does not need any options, you can define it as a function for the sake of simplicity.
<script>
import { loginApi } from './api';
export default {
name: 'Login',
asyncActions: {
login() {
return loginApi();
}
},
};
</script>Options
| Property | Description | type | Required | Default |
| ----------- | ----------------------------------------------------------------------- | -------- | -------- | ------- |
| handler | action's handler | function | true | |
| immediate | determines handler function should be called immediately after creation | boolean | false | false |
| debounce | debounce time in miliseconds | number | false | 0 |
| initialData | initial value of data property of action | any | false | null |
2. Create asyncActions outside of components
In this way, you can create asyncActions anywhere and use them as regular functions.
// usersActions.js
import { asyncAction } from '@cafebazaar/async-actions/vue';
import { someApiCall } from './api';
export const getUsers = asyncAction(() => someApiCall(), {
initialData: [],
});And after that, you can import and use it inside Vue components:
<template>
<div>
<div v-if="getUsersAction.state === 'pending'">
Fetching Users List. Please Wait...
</div>
<div v-else-if="getUsersAction.error">
Oops. Somthing Went Wrong :(
</div>
<div v-else>
<ul>
<li v-for="user in getUsersAction.data" :key="user.id">
{{ user.name }}
</li>
</ul>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { getUsers } from './usersActions';
export default {
name: 'UsersList',
computed: {
getUsersAction(){
return getUsers;
}
},
created(){
getUsers();
}
};Svelte
In the Svelte version, Store.writable is used for every observable prop(state, data, and error) and, you don't need to provide observableFn. You can simply do:
<script>
import asyncAction from '@cafebazaar/async-actions/src/svelte';
let myPromise = asyncAction(function () {
return new Promise((resolve) => {
setTimeout(() => resolve('My Data!!'), 5000);
});
}, options);
let { state, data, error } = myPromise;
// execute async function
myPromise();
</script>
<main>
<ul>
<li>Status: {$state}</li>
<li>Data: {$data}</li>
<li>Error: {$error}</li>
</ul>
</main>The List of all options is available here.
You can use asyncAction outside of svelte file and import it and use it directly inside DOM.
Pure JS
You can define an async-action using asyncAction method which gets a handler function and configuration options as its parameters. When using the pure version, you must provide an observable function which used for updating action properties.
import { asyncAction } from '@cafebazaar/async-actions/pure';
import customObservable from 'utils/observable';
const myAsyncAction = asyncAction(
Promise.resolve('Hello'),
options,
customObservable
);List of all options are available here.
